Advantages and Disadvantages of Biomass Energy + Facts You Should Know
by Tyler Castle
6.9 min read

Biomass energy is an increasingly popular form of renewable energy that harnesses organic materials to generate power. While it offers several environmental and economic advantages, there are also notable challenges to consider. We’ll explore the pros and cons of biomass energy, providing essential facts to help you understand its role in the global energy landscape.
What is biomass energy?
Biomass is a renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. Biomass is primarily used for heating and electricity generation and can even be used as transportation fuel. Until the 1800s biomass energy, was the largest primary energy source! In 2023, biomass energy accounted for 5% of total energy consumption.
Biomass is converted into energy through various processes:
Burning: Biomass can be combusted in a boiler to produce a stream of steam that is carried to a series of turbine blades. The stream causes the wind turbines to spin driving a generator that produces electricity.
Decomposition: With the absence of oxygen, organic materials are decomposed by anaerobic bacteria that produces methane. With these materials combined, natural gas can form.
Fermentation: Particularly sugar- and starch-rich materials are fermented to produce ethanol, a biofuel that can be blended with gasoline for transportation.
Types of biomass energy sources
- Wood like wood waste, sawdust
- Crops like corn, sugar cane, algae, soybeans
- Municipal solid waste products like cotton, wool products, and some paper products
- Waste like animal manure and human sewage
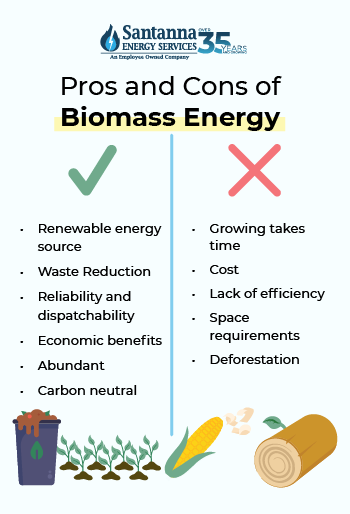
Pros of biomass energy
Biomass energy offers numerous pros, making it a valuable renewable resource in the shift toward sustainable energy.
Renewable resource
Unlike fossil fuels, which are non-renewable and are being depleted rapidly, biomass materials can be replenished on a much shorter time scale. Biomass can also be converted into liquid fuel as well making it versatile for various energy needs which can reduce the world’s overall reliance on fossil fuels.
As long as plants grow continuously and proper waste management is achieved, biomass can be sustainably harvested to generate energy without exhausting natural reserves.
Waste reduction
Another pro of using biomass energy is its promotion of waste reduction. Certain waste like sawdust and paper products can be repurposed into electricity, heat, or biofuels. This reduces the amount of garbage waste that ends up in landfills and provides no extra value to the environment.
Similarly, when waste decomposes, it secretes harmful methane gas that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. By utilizing waste products and converting them safely into usable energy, biomass energy helps prevent the release of methane into the atmosphere, reducing its impact on climate change.
Reliability and dispatchability
Biomass energy can be generated on demand and provide consistent energy when needed. In contrast to wind energy and solar energy, biomass energy doesn’t have to depend on weather conditions to produce its energy. As long as organic material is available, biomass energy can be classified as reliable and predictable to meet growing demand.
Economic benefits
Biomass provides additional revenue for waste and organic material producers. The creation of biomass energy allows these producers to sell materials like agricultural residues, wood chips, or food waste that would otherwise be discarded.
In the same way, producing biomass energy can lead to the creation of more green jobs. Not only will biomass plants feel a positive impact, but industries like agriculture and manufacturing can benefit from this too as they are integral to producing sources to create this energy source. According to the Department of Energy, biomass energy is reported to create over 1 million jobs by 2030.
Abundant
Another pro of this energy source is that biomass can be made from an abundance of materials. Biomass can come from organic materials, including agricultural residues like crop waste, wood from forests, animal manure, food scraps, and even specific energy crops grown specifically for fuel production. This variety allows biomass energy to be produced in marginal lands, leveraging local resources and reducing transportation costs.
Carbon neutral
Biomass energy prevents greenhouse gases from being emitted from other sources. By converting organic material into biomass energy before it decomposes reduces the amount of greenhouse gases into the air. Additionally, biomass energy can offset emissions from fossil fuels by providing a renewable alternative for electricity, heat, and transportation fuels. Because biomass, when sustainably managed, absorbs carbon dioxide during its growth, it can create a more balanced carbon cycle.
Cons of biomass energy
Like any energy source, biomass energy comes with disadvantages. Here are some of the most common:
Growing takes time
Biomass relies on the production of organic materials, primarily wheat. While biomass energy can be more reliable than traditional fossil fuels, biomass feedstocks need to be cultivated, harvested, and processed before they can be used for energy production. This can create delays in availability depending on growing conditions and crop cycles.
Cost considerations
Biomass energy can be expensive to produce because it’s not the most widely used renewable energy resource at the moment. There are higher costs associated with collection, transportation, and storage compared to other renewable resources like wind or solar. Additionally, the technology used to convert biomass into usable energy, such as gasification or anaerobic digestion, may involve high capital investments and operational expenses.
Efficiency issues
Biomass energy is generally less efficient compared to fossil fuels and other renewable sources. For example, biofuels have to be mixed with fossil fuels to increase their efficiency. Additionally, the energy conversion processes for biomass, such as combustion, gasification, or fermentation, can have lower efficiencies compared to technologies that might result in energy loss.
Space requirements
Biomass energy plants require a significant land area. Large tracts of land are needed to grow crops specifically for energy production. Additionally, transporting biomass sources can lead to high transportation costs. While biomass plants are concentrated in mostly rural areas, biomass production can be limited to densely populated areas or regions with limited available land.
It can cause deforestation
Another biomass energy disadvantage is the potential deforestation effects. While biomass energy is made from organic materials like trees and crops, these organic materials are harvested in large batches. This large-scale harvesting can lead to deforestation if not managed sustainably. Similarly, to make way for these fields of organic matter, the demolition of forests might be required.
This can lead to the disruption of ecosystems and vital forest cover.
Comparisons with other energy sources
Renewable Energy Sources Compared
| Solar Energy | Wind Energy | Geothermal Energy | Biomass Energy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment. Can breakeven after 10 years. | Moderate initial investment; low ongoing costs. | High initial investment; low ongoing costs. | High initial investment; higher ongoing costs due to collection & transportation |
| Dispatchability | Intermittent; generates power only during sunlight hours. | Intermittent; depends on wind speeds and weather conditions. | Reliable and consistent; generates power continuously. | Reliable and dispatchable; can provide power on demand. |
| Emissions | Very low. | Very low. | Very low. | Very low. |
| Space Requirements | Requires significant space for large-scale installations. | Requires large areas for wind farms. | Requires specific geological conditions; smaller land footprint. | Requires significant land for cultivation of crops. |
| Efficiency | Variable. | Variable. | High. | Generally lower efficiency compared to geothermal and wind. |
| Storage Requirements | Often requires energy storage. | Often requires energy storage or backup systems. | Minimal storage required. | Minimal storage needed. |
Fun Facts about Biomass
While biomass energy has its pros and cons, here are some fun facts about this energy source that make investing in biomass worthwhile:
- Three million chickens in Beijing produce 220 tons of manure and water waste each day to make biomass electricity.
- The first biomass gasification plant was opened in 1998.
- The world’s top biofuel crops include wheat, switchgrass, sunflowers, and soy!
- By 2030, the U.S. has the potential to generate 1 billion tons of biomass energy.
- Algae-based fuels can be produced 5-10 times faster than biomass energy produced by soy or corn.
There’s peace of mind in knowing you’ll pay the same monthly supply cost amount for your electricity or natural gas supply without any uncertainty — no matter what. Santanna’s Unlimited Energy option protects your bills from fluctuating supply charges no matter the changes in seasons. For over 35 years, Santanna has served customers in Illinois, Indiana, Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Ohio. Our mission is to provide innovative and cost-effective energy solutions that will help our customers achieve their energy goals.
Tyler is an experienced energy professional, having worked for Santanna Energy Services, for the past four years. He is passionate about renewable energy and believes that diversifying the energy grid is the key to a sustainable future. Tyler is dedicated to supplying consumers with the best possible energy solutions and works diligently to make sure that Santanna can deliver the highest quality service.