Differences Between El Nino and La Nina: La Nina 2024 Impacts
by Tyler Castle
10.7 min read

El Nino and La Nina are two powerful climate phenomena that shape global weather patterns, affecting everything from rainfall and snowfall to drought and extreme temperatures. These phases, part of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, lead to starkly different impacts.
Understanding these patterns is essential for preparing for weather events, managing agriculture, and adapting to potential changes influenced by climate change. Let's take a look at the differences between these two weather patterns and dive into predictions for La Niña 2024 and 2025!
Key Points of This Article:
- El Niño warms Pacific waters, weakens winds, and brings wetter winters to North America.
- La Niña cools waters, strengthens winds, and causes colder, snowier winters in the northern U.S.
- In 2024, El Niño drove record warmth; La Niña was predicted to return later.
- For 2025, NOAA expects wetter northern U.S., drier southern states, and colder Midwest winters.
What is El Nino?
El Nino is a climate phenomenon marked by the warming of ocean surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. This shift disrupts typical weather patterns globally, leading to increased rainfall in some regions and drought in others. During El Nino, trade winds weaken, allowing warmer water to spread eastward across the Pacific.
What is La Nina?
La Niña is the opposite phase of El Niño, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific. During La Niña, trade winds strengthen, pushing warmer surface waters westward and allowing cooler, deeper waters to rise in the east. This can lead to intensified weather conditions making things colder and wetter in some regions.
Explaining El Nino and La Nina at a 5th-grade reading level
Having trouble with the difference between El Niño and La Niña? No worries, we’ve got you!
In a less technical sense, imagine the Pacific Ocean as a giant bathtub with water that moves and changes temperature. During La Niña, you’re adding cold bath water; imagine the ocean turning into a chilly swimming pool! The water near South America becomes much cooler than normal.
Because of the shift of the jet stream, during La Niña, you might see more hurricanes and colder winters in some parts of the US.
Now, think of El Niño as warm bath water being dumped in the Pacific Ocean. Normally, the ocean’s water is cooler near South America and warmer near Asia. But during an El Niño, the water near South America gets much warmer than usual. It’s like the ocean is taking a warm bath!
This warm water changes how winds blow and can cause more rain in places like California, fewer hurricanes in the Atlantic, and warmer winters in some parts of the US.
What’s the difference between El Nino and La Nina?
The main difference between El Nino and La Nina is in the direction and intensity of temperature changes in the Pacific:
El Nino brings warmer-than-normal sea surface temperatures, weakened trade winds, increased rainfall in some regions, and dry conditions in others.
La Nina brings cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures, strengthened trade winds, and opposite impacts on weather patterns compared to El Nino.
The difference between El Nino and La Nina lies in their contrasting effects on global weather. Together, they form a climate cycle that can influence temperature, precipitation, and storm activity worldwide.
La Nina vs El Nino: how do they affect the weather?
Both El Niño and La Niña have global weather impacts:
El Niño often brings warmer, wetter winters to North America, more rainfall to the southern U.S., and increased drought conditions in Australia and Southeast Asia.
La Niña can cause cooler and wetter conditions in the Pacific Northwest, drier weather in the southern U.S., and more tropical cyclones in the Atlantic.
What happens during El Nino?
During El Nino, ocean temperatures rise in the central and eastern Pacific, which can cause:
- Increased rainfall in typically dry areas (like the southwestern U.S.)
- Drought in areas that normally receive regular rain, such as Australia and Indonesia
- Potential for stronger and more frequent storms, including hurricanes and typhoons
Overall, there are warmer winters in some parts of the United States.
What happens during La Nina?
La Niña typically brings:
- Warmer, drier weather in the southern U.S., which can increase drought conditions
- Increased rainfall in places like Southeast Asia and northern Australia
- Colder winters in some parts of North America.
How long do El Nino and La Nina Typically Last?
Both El Niño and La Niña events usually last 9-12 months, though some can extend up to two years.
They typically begin developing in spring, intensify through the year to peak during winter, and gradually weaken by the following spring. Occasionally, a strong event may continue into a second year, creating extended impacts on global weather, agriculture, and ecosystems. The timing and duration of these events vary, but the strongest effects are generally seen in winter.
How often Do El Nino and La Nina episodes happen?
El Niño and La Niña episodes typically follow a 2–7-year cycle, known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). However, each cycle’s exact timing and intensity can vary widely.
What was the biggest impact we’ve seen from El Nino and La Nina in 2024?
The impacts of El Nino and La Nina for 2024 took place mostly in the early months of the year. While there was a predicted La Nina predicted for early 2024, El Nino dominated the first half of 2024. This El Nino led to record setting warm temperatures in January and February and the rest of 2024. The impacts of La Nina in late 2024 are yet to come.
Will La Nina return in 2024?
As of October 10th, 2024, forecasters continue to favor a return of La Nina in 2024 later this year. Weather personnel predict an approximate 60% chance of development of La Nina in 2024. The next report on updated predictions that report on La Nina 2024 will be released in mid-November 2024.
La Nina in the later months of 2024 will be less than previously predicted. There have been stretches of colder water and stronger than average trade winds in the pacific that could indicate a La Nina return during the remaining months of 2024.
La Nina 2025 predictions
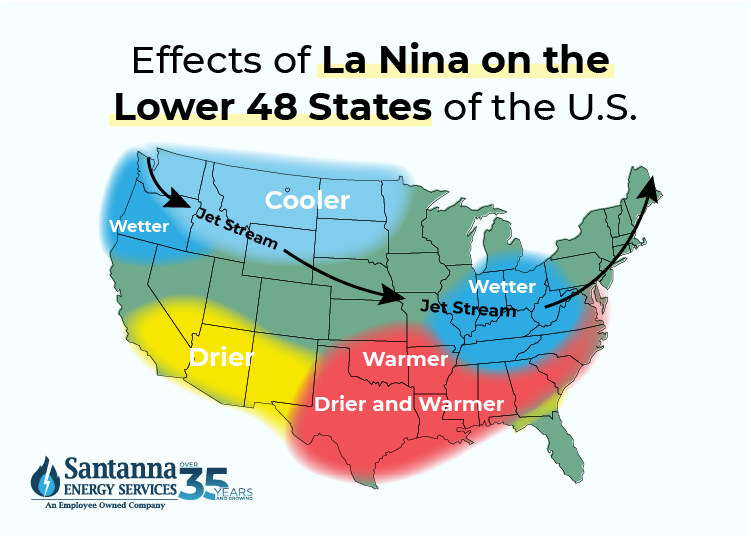
N.O.A.A predicts wetter-than-average conditions for the entire northern tier of the continental U.S., particularly in the Pacific Northwest and the Great Lakes region. This is especially true in portions of Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky. Wetter conditions are a strong sign of a La Nina in 2025.
From the same report, warmer-than-average temperatures are favored from the southern tier of the U.S. to the eastern Great Lakes while Alaska will see below average temperatures. With this, drier conditions are predicted for the Southwest, Southeast, Gulf Coast, and lower Mid-Atlantic states.
The winter months in the contiguous 48 states could be filled with frequent weather changes from week-to-week rather than prolonged periods of more consistent weather. Large portions of the northern US are expected to end up wetter than normal this winter, especially the Pacific Northwest and Midwest indicative of a La Nina in 2025.
Does La Nina mean colder winters?
Yes, La Nina does mean colder winters. La Nina often brings colder winters to certain regions, especially the northern parts of North America. For example, the northern U.S. and Canada may experience colder-than-average temperatures, while the southern U.S. tends to see warmer, drier conditions.
States like Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, and regions in New England often experience prolonged cold spells.
Colder winters associated with La Niña may also see more frequent polar vortex occurrences, bringing frigid air masses from the Arctic into northern U.S. regions and even extending into parts of the Midwest and Northeast.
Is El Nino or La Nina better for snow?
La Niña tends to produce more snow in the northern U.S. and Canada due to its colder conditions, especially in regions near the Great Lakes and in the Pacific Northwest.
Conversely, El Niño is often warmer and can result in less snow overall, although some southern and coastal areas might see increased precipitation.
Mountain ranges like the Cascades, the northern Rockies, and the Sierra Nevada often see above-average snowpack during La Nina and will see this again if La Nina 2024 returns. Lake-effect snow can lead to significant accumulation, especially during the peak of winter during La Nina. All these reasons lead to La Nina being better for snow.
Does La Nina mean more snow?
Yes, La Nina does mean more snow. La Niña generally increases snowfall in colder northern regions of North America, especially in the Pacific Northwest, the northern Rockies, and parts of the Midwest due to colder, wetter conditions.
In the Pacific Northwest: La Niña usually results in wetter, colder conditions, which enhance snow accumulation in mountain ranges such as the Cascades.
In the Northern Rockies: La Niña often brings above-average snowfall to mountainous areas, benefiting ski resorts and water reservoirs but sometimes causing avalanche concerns.
In the Great Lakes and Midwest: The northward shift in the jet stream allows for cold air and moisture from the lakes, producing intense lake-effect snow, particularly in areas near the Great Lakes.
In the end, La Nina does mean more snow for mountains and northern states and parts of the U.S.
La Nina Midwest: Does La Nina affect the Midwest?
Yes, La Nina affects the Midwest by typically bringing colder and snowier winters. However, it may also lead to drier spring and summer conditions, which can influence crop yields and water resources in the region. La Nina in the Midwest leads to:
Increased Snowfall: During La Nina, the Midwest frequently sees above-average snow totals, especially in states like Michigan, Wisconsin, and Illinois. This snowfall can be beneficial for soil moisture but may challenge infrastructure and transportation.
Colder Winter Temperatures: The southward jet stream path brings colder-than-usual winter conditions across much of the Midwest, which can increase heating demands and strain energy resources.
Spring and Summer Impacts: La Niña’s influence can extend beyond winter. The Midwest often experiences drier conditions in spring and summer after a La Niña winter, which may reduce soil moisture levels, impacting crop health and water availability for agriculture.
El Nino Midwest: What are those effects?
The Midwest region is also affected by El Nino. El Nino in the Midwest usually brings
Warmer, Drier Winters: El Niño typically brings warmer-than-average winter temperatures to the Midwest, which can reduce snow cover and decrease the risk of winter storms in many areas.
Drier Spring and Summer Conditions: The warmer, drier winter conditions can sometimes carry into spring, leading to reduced soil moisture levels that may affect crop planting and growth.
Decreased Risk of Tornadoes: The Midwest often experiences fewer severe storms and tornadoes in the spring and summer months thanks to the impact of El Nino.
Why do the El Nino and La Nina climate patterns matter?
El Niño and La Niña matter because they influence global weather, agriculture, water resources, and disaster preparedness. These climate patterns affect rainfall, drought, and storm patterns worldwide, impacting ecosystems, economies, and daily life.
El Niño and La Niña patterns affect crop production globally by altering precipitation and temperature patterns. Farmers in areas like the U.S. Midwest must adapt to these changing conditions to manage crop yields.
Shifts in precipitation and temperature can disrupt ecosystems and biodiversity. Warmer El Niño events, for instance, have been known to cause coral bleaching, while La Niña’s increased rainfall can flood certain habitats.
Both El Niño and La Niña significantly impact weather systems worldwide, influencing rainfall, droughts, and temperatures that can affect ecosystems, economies, and daily life. While El Niño brings warmer temperatures and alters precipitation patterns, La Niña is associated with colder, wetter conditions in many regions, often leading to increased snowfall and cooler winters.
As climate change may intensify these patterns, understanding and monitoring ENSO events becomes increasingly important for disaster preparedness and resource management worldwide.
Make an impact on the planet through your energy choice. Santanna Energy Services offers Earth Friendly Gas Plans that helps you create ecological balance in the world through carbon offsetting: making up for our emissions here by reducing emissions elsewhere. So, simply by heating your home, you can be helping the planet.
Santanna Energy Services is a supplier of earth-friendly natural gas and electricity solutions for your home. For over 35 years, Santanna has served customers in Illinois, Indiana, Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Ohio. Our mission is to provide innovative and cost-effective energy solutions that will help our customers achieve their energy goals.
Tyler is an experienced energy professional, having worked for Santanna Energy Services, for the past four years. He is passionate about renewable energy and believes that diversifying the energy grid is the key to a sustainable future. Tyler is dedicated to supplying consumers with the best possible energy solutions and works diligently to make sure that Santanna can deliver the highest quality service.