Electric vs. Gas Furnaces: What To Know
by Tyler Castle
21.3 min read
When it comes to heating your home, choosing between an electric and gas furnace is one of the most important decisions a homeowner can make. Each type of furnace offers distinct advantages in terms of cost, efficiency, and overall performance, but knowing which option is right for your home depends on a variety of factors.
If you need energy but you’re unsure if a gas or electric furnace is right for you, keep reading! We’ll break down everything you need to know about electric vs. gas furnaces, helping you understand key differences and more. Whether you’re looking to make a new purchase or simply want to understand how your current system works, we’ll help you make an informed decision tailored to your home and lifestyle.
Key Points of This Article:
- Electric furnaces are easier to install, require less maintenance, last longer, and work best in mild climates, while gas furnaces provide stronger heat and lower operating costs in colder regions.
- Electric furnaces use resistance heating and offer nearly 100% efficiency, whereas gas furnaces rely on combustion, heat exchangers, and venting, which can reduce efficiency slightly.
- Gas furnaces heat faster and cost less to run but have higher installation costs, shorter lifespans, and added safety risks such as carbon monoxide leaks.
- Choosing between electric and gas depends on climate, budget, efficiency needs, environmental impact, and long‑term operating costs, often requiring professional guidance for the best fit.
What to Know About Electric vs. Gas Furnaces
Looking to learn the full breakdown of electric vs. gas furnaces? In terms of warming your residence, this is a choice that should not be taken lightly. Both options come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s cover the main differences between electric furnaces vs gas furnaces:
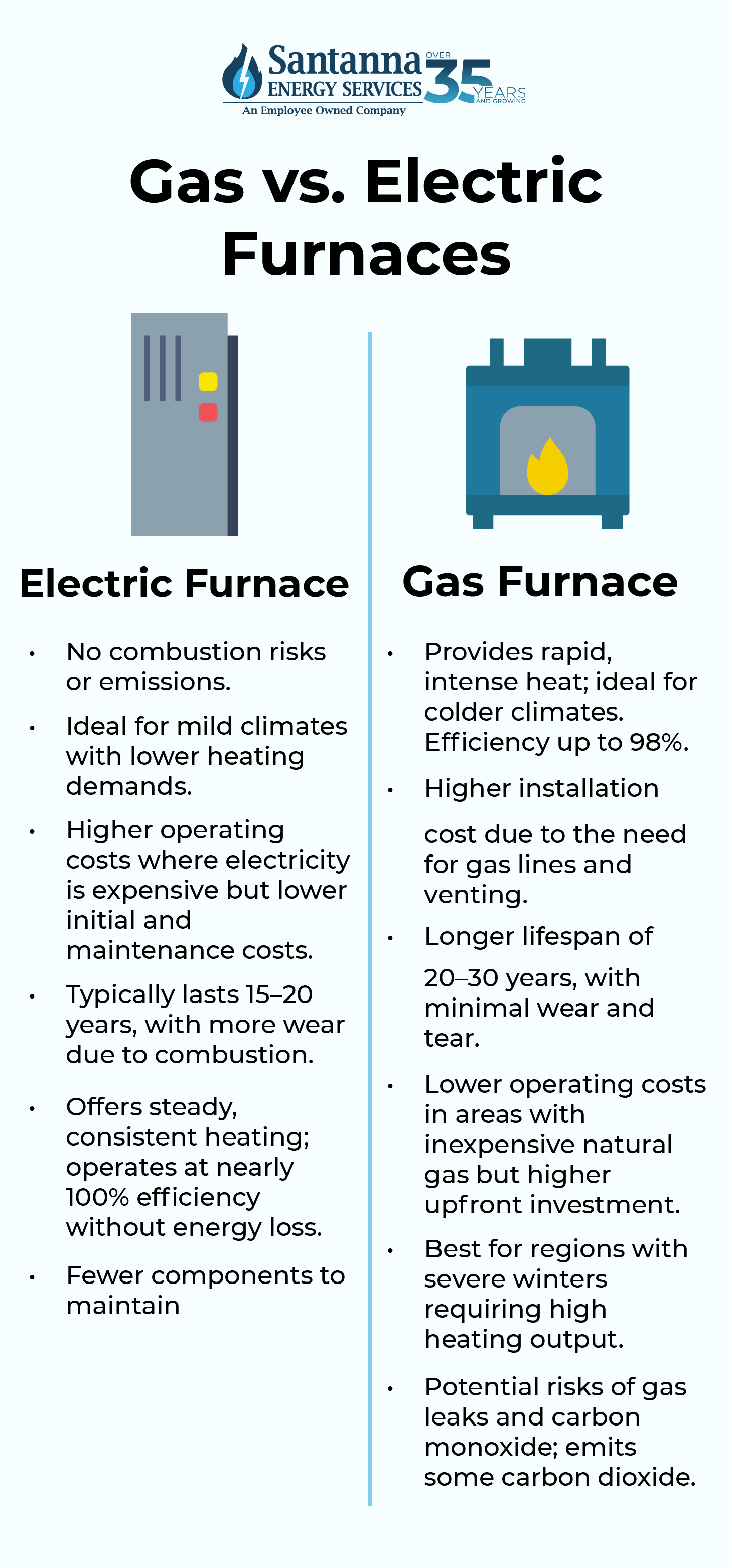
Electric Furnaces
If you’re torn between electric vs gas furnaces, it’s important to know that electric furnaces generally have simpler installation requirements since they don’t need gas lines or venting, making them more affordable to install initially. In the same way, without combustion, electric furnaces have fewer components that wear down, reducing maintenance needs over time.
Electric furnaces often last 20–30 years, as they experience less wear and tear compared to gas units. Electric furnaces are best suited to mild climates where high heating demands are infrequent, as they produce heat more gradually. In regions where electricity is more affordable or where renewable energy is available, electric furnaces can be a cost-effective option for home heating.
Gas Furnaces
If you’re considering a gas furnace as opposed to an electric furnace there are a few things you should know. Gas furnaces produce more intense, consistent heat, making them ideal for regions with severe winters. Operating costs for gas furnaces can be lower in areas where natural gas is inexpensive, providing a more budget-friendly option over time.
Newer high-efficiency gas furnaces can achieve AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings of up to 98%, making them competitive with electric options in terms of energy use. Unfortunately, gas furnaces typically last 15–20 years, as the combustion process creates wear on internal components. Lastly, gas furnaces can lower indoor humidity, which can be beneficial in humid climates but may require a humidifier in drier regions.
How Does an Electric Furnace Work?
If you’re wondering how an electric furnace works, we’ve got you covered! Electric furnaces work by using metal heating elements, typically made of materials like nickel-chromium alloy, that act as resistors. When electricity flows through these elements, they resist the flow of electric current, causing them to heat up. This process is known as electric resistance heating and converts almost all of the electric energy directly into heat.
To distribute the heat throughout your home from an electric furnace, a blower fan circulates air across the heated coils, warming the air as it passes over them. The warm air is pushed through the home’s duct system and dispersed into each room via vents.
Electric resistance heating is 100% energy efficient in the sense that all incoming electric energy is converted to heat; however, it may have higher operational costs in regions where electricity is more expensive than natural gas.
How Does a Gas Furnace Work?
On the flip side, if you’re wondering how a gas furnace works, keep on reading. Gas furnaces work by using a burner that ignites natural gas or propane fuel. When the thermostat calls for heat, a valve opens to release gas into the burner, and the ignition system (pilot light or electric igniter) lights the gas. The combustion process creates heat, which raises the temperature in the furnace.
The air in your home begins to warm through the heat exchanger in your gas furnace. The heat exchanger is a metal chamber or series of coils within the furnace that absorbs heat produced by combustion. The heat exchanger ensures that no combustion gases enter the airflow, making the air safe and clean for home heating. As the gas burns, hot combustion gases flow through the heat exchanger, transferring heat to the metal walls of the exchanger.
The combustion gases then exit the furnace through a flue or vent to the outside, while the heated exchanger remains in the furnace. Next, a blower fan pulls cooler air from the home, moves it across the hot heat exchanger, and circulates the now-warmed air through the ductwork and into living spaces.
Gas furnaces are known to heat up quickly and produce warmer air than electric furnaces, making them effective for colder climates. However, they do lose some heat through the venting system, which can slightly reduce efficiency compared to electric models. Gas furnaces typically have AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings that reflect their efficiency, which varies by model and insulation.
Pros and Cons of an Electric Furnace vs. Gas Furnace
When it comes to choosing between electric and gas furnaces, understanding the pros and cons of each is crucial for making an informed decision. Both types of furnaces have unique benefits and potential drawbacks that can impact your comfort, budget, and energy efficiency.
Pros of Electric Furnace
Lower Initial Cost: Electric furnaces are typically more affordable upfront than gas furnaces, offering a budget-friendly way to maintain a warm, comfortable home.
Long-Lasting: With lifespans often reaching 20 to 30 years, electric furnaces provide a durable heating solution that’s worth considering for those investing in a new system.
Ease of Use and Maintenance: Operating an electric furnace is simple—just adjust the thermostat. They also require minimal maintenance, making them a low-effort heating option.
Cons of Electric Furnace
Higher Operating Costs: Electric furnaces generally cost more to run than gas models, which can add up over time on energy bills.
Dry Heat: Electric furnaces produce a dry warmth, which can reduce indoor humidity during winter. This can be uncomfortable for some, especially those with allergies or sensitivities to dry air.
Slower Heating Performance: Electric furnaces typically take longer to heat a space compared to gas furnaces. This is because electric systems may not generate heat as rapidly as combustion-based systems, which can be noticeable during extremely cold weather.
Pros of Gas Furnace
Lower Operating Costs: Over time, gas furnaces tend to be more cost-effective than electric models due to lower fuel prices, making them a budget-friendly choice for long-term use.
Quicker Heating: Gas furnaces provide rapid, consistent warmth, making them ideal for colder climates where maintaining a cozy indoor temperature is essential.
Wide Availability of Natural Gas: Natural gas is widely accessible, and having multiple suppliers in many areas allows homeowners to shop around for competitive pricing.
Cons of Gas Furnace
Carbon Emissions: Although gas furnaces burn cleaner than many other fuel types, they still produce a small amount of carbon dioxide. If the system malfunctions, carbon monoxide levels could rise, posing health risks.
Higher Installation Costs: While gas furnaces typically cost less to operate, they can be more expensive to install than electric furnaces, which may require time to offset the upfront investment.
Shorter Lifespan: Gas furnaces generally have a shorter service life, often requiring replacement after 10–15 years, compared to the 20–30 years typical for electric units.
Space Requirements for Ductwork: Gas furnaces often need larger, bulkier ductwork, which can be challenging to fit into smaller spaces or older homes when considering a conversion to natural gas.
Cost Comparison of a Gas and Electric Furnace
When choosing between electric and gas furnaces, it’s essential to consider various cost factors, including upfront equipment and installation expenses, monthly utility costs, and long-term maintenance. Below is an average cost estimate as of 2024:
Costs of an Electric Furnace vs Gas Furnace
| Cost Aspect | Electric Furnace | Gas Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Cost | Ranges from $1,000 to $2,500. | Ranges from $3,000 to $4,000. |
| Installation Cost | Averages between $1,000 and $1,500. | Averages between $1,500 and $2,000. |
| Utility and Operating Costs | Higher due to electricity rates; for example, in the Midwest, the average annual cost for electricity is $1,260.
Electricity costs vary by region, affecting overall expenses. |
Generally lower because natural gas is often less expensive; in the Midwest, the average annual cost for gas is $665.
Natural gas prices fluctuate regionally, influencing operating costs. |
| Maintenance Cost | Lower due to fewer moving parts and no combustion process. | Higher because of the combustion process and more complex components. |
Safety Considerations: Electric vs Gas Furnaces
When choosing a furnace, safety is a top priority, and each type of furnace has unique safety features and risks that homeowners should consider. While electric furnaces generally present fewer risks due to the absence of combustion, gas furnaces can be more prone to specific safety hazards. Here’s a breakdown of the key safety considerations for each furnace type.
Electric Furnace Safety
Electric furnaces do not rely on burning fuel, so there’s no risk of combustion-related hazards, such as gas leaks or fires caused by a flame. Additionally, electric furnaces produce no carbon monoxide, a dangerous, odorless gas. This makes them safer in terms of air quality and health.
While electric furnaces are generally safe, electrical components can still pose risks if damaged. Homeowners should ensure that wiring is up to code, use properly rated circuit breakers, and arrange for regular inspections by a qualified technician to prevent electrical malfunctions.
Gas Furnace Safety and Carbon Monoxide Risks
Gas furnaces rely on combustion to generate heat, which involves burning natural gas or propane. While safe when installed and maintained properly, any malfunction in the fuel system, gas line, or heat exchanger can lead to gas leaks. If unnoticed, these leaks pose serious safety and health risks.
Gas furnaces can emit carbon monoxide if combustion doesn’t fully occur or if the heat exchanger develops cracks. Carbon monoxide detectors are crucial to alert residents to any leaks, as carbon monoxide is invisible and odorless but highly toxic. Regular inspections are essential to ensure the integrity of the heat exchanger and venting system.
Fire Prevention and Safety Tips
For both electric vs gas furnaces, professional installation is critical to minimize risks. Improper installation can lead to wiring issues in electric furnaces or fuel and exhaust problems in gas furnaces.
Scheduling annual maintenance by a certified technician can help detect and resolve potential safety issues, such as frayed wires which can lead to electrical fires in electric furnaces or cracked heat exchangers in gas furnaces.
Equally as important, it’s essential for homes with gas furnaces to have carbon monoxide detectors in key areas. These detectors sense when CO levels reach dangerous concentrations in the air, which occurs when fuel-burning appliances malfunction or aren’t properly vented.
Efficiency Ratings and Performance
Recent price data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics shows that the national average cost for natural gas in 2024 was $1.40 per therm, compared to typical residential electricity rates of around $0.18 per kWh. Efficiency is a crucial factor in determining the long-term cost-effectiveness and environmental impact of a furnace, and both electric and gas furnaces have their respective strengths in this area.
Electric Furnace Efficiency
Electric furnaces operate at nearly 100% efficiency because they convert all electricity into heat. Unlike gas furnaces, which lose a portion of energy through exhaust gases, electric furnaces don’t require combustion, meaning there’s no energy loss due to venting. The metal heating elements effectively transfer electricity into heat, providing consistent efficiency throughout the furnace’s lifespan.
Gas Furnace Efficiency
High-efficiency gas furnaces today can reach up to 98.5% efficiency, converting nearly all fuel into usable heat. This high rating means only around 2% of energy is lost through exhaust gases or heat dissipation. However, as gas furnaces age, components can wear out, leading to a gradual reduction in efficiency. Regular maintenance is essential to preserve efficiency and prevent higher energy bills as the furnace ages.
Comfort and Air Quality
The comfort and indoor air quality provided by an electric vs gas furnace plays a significant role in the overall health and livability of your home. Electric and gas furnaces impact temperature control and humidity differently and understanding these distinctions can help homeowners choose the best option for their specific needs.
Comfort with Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces often provide steady, consistent heat, as they cycle on and off with precise control. This helps maintain a stable indoor temperature without significant fluctuations, contributing to a more comfortable living environment.
Unlike gas or oil furnaces, electric furnaces don’t burn fuel to generate heat, releasing no combustion byproducts. This means no carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, or other toxins are released into your home, reducing the risk of indoor air pollution and improving overall air quality.
Comfort with Gas Furnaces
Gas furnaces produce warm air quickly through combustion, which can warm a home faster than electric models. However, the combustion process tends to reduce humidity levels in the air. This drying effect can be beneficial in humid climates, where homeowners may prefer the dehumidifying effect of a gas furnace. In drier regions or during cold seasons, this reduction in humidity can create discomfort for some, requiring the use of a humidifier.
Gas furnaces can impact air quality, as combustion byproducts, including small amounts of nitrogen dioxide, can enter the home if the system is not properly vented or maintained. Additionally, gas furnaces can distribute dust and particulates through the ductwork. Ensuring that air filters are regularly replaced and the system is vented correctly can help maintain good air quality.
Air Quality and Humidity Comparison
Electric furnaces tend to have fewer impacts on indoor air quality, as they don’t release combustion byproducts. They’re often preferred by those with respiratory sensitivities or allergies. Gas furnaces, on the other hand, may require additional ventilation and air filtration to ensure that combustion byproducts don’t affect indoor air.
Furnaces can lower humidity, which is beneficial in humid regions but may cause dry air discomfort in dry areas or during winter months.
Environmental Impact
When considering heating options, environmental impact is an essential factor, as heating systems contribute to carbon emissions and overall environmental footprint. Here’s a breakdown of how gas and electric furnaces compare in terms of environmental impact, along with the added perspective of heat pumps as a sustainable alternative.
Gas Furnace Environmental Impact
Gas furnaces rely on burning natural gas or propane, which directly releases carbon monoxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. While gas furnaces can be efficient, this combustion process contributes to air pollution and increases carbon emissions.
The combustion of natural gas not only produces CO₂ but also releases nitrogen oxides, which can degrade air quality. Proper ventilation is needed to safely expel these gases.
As a non-renewable energy source, natural gas contributes to resource depletion. Although modern high-efficiency gas furnaces minimize energy waste, they still depend on a fossil fuel, limiting their sustainability.
However, homeowners can reduce their environmental impact by choosing Santanna Energy Services’ Earth-Friendly natural gas plan, which helps offset emissions while providing heating! This option allows you to enjoy the benefits of gas heating with a more earth-friendly approach.
The combustion of natural gas not only produces CO₂ but also releases nitrogen oxides, which can degrade air quality. Proper ventilation is needed to safely expel these gases.
Electric Furnace Environmental Impact
Unlike gas furnaces, electric furnaces do not produce carbon monoxide or other combustion-related emissions, making them cleaner from an indoor air quality perspective.
The environmental footprint of electric furnaces largely depends on the source of electricity. If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, the furnace indirectly contributes to carbon emissions. However, when powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind, electric furnaces can be a more sustainable option.
How Long Does a Gas Furnace Last?
A gas furnace’s lifespan typically ranges from 15 to 20 years, depending on the quality of the unit, the installation, and the level of maintenance it receives over time.
Key parts, such as the heat exchanger, burners, and ignition system, may experience wear from constant exposure to combustion byproducts and high heat. Regular maintenance—such as annual inspections, cleaning, and timely repairs—can help extend the life of a gas furnace by addressing issues before they lead to larger failures.
How Long Does an Electric Furnace Last?
Electric furnaces are known for their longevity, often lasting 20 to 30 years or more with proper care.
Unlike gas furnaces, electric models do not rely on combustion, which reduces strain on components and minimizes exposure to heat damage or corrosion. The primary parts of an electric furnace—such as heating elements, blower motor, and controls—tend to be more durable and can withstand extended use without significant degradation.
Gas vs. Electric Furnace Impact on Home Resale Value
The type of furnace in your home can significantly influence its resale value, as prospective buyers often consider long-term energy costs and system reliability when making a decision. Here’s how your furnace choice can appeal to potential buyers:
Resale Value with Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces are seen as more eco-friendly, especially if powered by renewable energy, making them attractive to buyers who prioritize sustainability. Homes with solar panels or other renewable energy sources pair well with electric furnaces, which can lower operational costs and boost appeal. Electric furnaces typically require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan, which can be a selling point for buyers wanting a low-maintenance, reliable heating option.
Resale Value with Gas Furnaces
In regions with long, harsh winters, buyers may prefer gas furnaces because of their quick, powerful heating capabilities. In areas where natural gas is more affordable, buyers may value gas furnaces for their lower monthly heating costs. For regions with high heating needs, a gas furnace may be seen as an essential feature, adding to the home’s overall value.
Heat Pump vs Furnaces
Heat pumps primarily use electricity to transfer heat, making them an efficient option for milder climates. Furnaces typically use natural gas, propane, or electricity to generate heat, making them ideal for colder regions where consistent warmth is essential.
While heat pumps are highly efficient, heat pumps can struggle in freezing temperatures to heat up. Furnaces on the other hand provide reliable and consistent heat, even during the coldest winter months. Heat pumps may have higher upfront costs and could increase electricity usage. Furnaces are often more cost-effective, especially for homes already equipped with natural gas lines.
Does a Gas Furnace Use Electricity?
Gas furnaces do need electricity to operate. Gas furnaces need a small amount of electricity to ignite (about 600 watts) as well as to operate the furnace blower, just like electric furnaces.
Gas furnaces use such a small amount of electricity, that to accurately measure their operating costs against electric furnaces, you’ll need to compare their fuel costs — i.e., how much electricity an electric furnace uses vs. how much natural gas a gas furnace uses. For an estimated calculation of this, keep reading here!
How to Tell if My Furnace is Gas or Electric
1. Check the Power Source:
Gas Furnace: Connected to a gas line or propane tank, which should be visible near the furnace or on the utility bill.
Electric Furnace: Connected only to an electrical supply; typically does not require any gas line or external fuel source.
2. Look for a Pilot Light or Ignition System:
Gas Furnace: Often has a pilot light or an electronic ignition system to ignite the gas. If you see a small burner or ignition component, it’s likely a gas furnace.
Electric Furnace: Lacks a pilot light, as it doesn’t require combustion to generate heat.
3. Inspect for a Flue or Vent Pipe:
Gas Furnace: Needs ventilation to expel combustion gases, so it will usually have a metal or plastic vent pipe leading outside.
Electric Furnace: Does not produce combustion gases, so it won’t have a flue or vent pipe.
4. Check the Thermostat Settings:
Sometimes, the thermostat or control panel near the furnace may indicate the type of system installed. For example, it might say “electric heat” or “gas heat.”
5. Check the Label or Manual:
The furnace’s model number, label, or owner’s manual often specifies whether it’s an electric or gas furnace.
6. Listen for Operation Differences:
Gas Furnace: May produce a soft ignition noise or slight “whoosh” sound as the gas ignites.
Electric Furnace: Operates quietly, with no combustion sounds.
Furnaces can be powered by electricity, gas, propane, or oil. They vary in size and efficiency, and more recent models have energy-saving features like modulating gas valves and variable-speed blowers. If you’re unsure whether your furnace runs on gas or electricity, finding it in your house is the first step to learning how it operates.
Can I Convert from a Gas Furnace to Electric (and Vice Versa)?
Yes, you can convert from a gas furnace to an electric one. The process involves several factors that should be carefully considered. Switching from gas to electric typically requires upgrades to your home’s electrical system, as electric furnaces demand higher voltage and amperage. Conversely, converting to a gas furnace may involve installing gas lines, venting systems, and meeting local building codes.
Here’s what else you should consider before making the switch:
Converting from a gas to an electric furnace
The initial step in converting a gas furnace to an electric furnace involves removing the existing gas unit. Although this might seem challenging, the process is fairly straightforward. Licensed contractors will first disconnect your home from the gas supply and then remove all current gas-related equipment.
Next, an HVAC technician will install the components needed for the electric furnace, which may involve upgrading your home’s electrical system to support the new unit. Generally, the existing ductwork can be used with the new electric system unless there are any issues that require it to be replaced.
Converting from an electric to a gas furnace
The first step is to install or activate a natural gas line in your home if one is not already available. This process will require coordination with your local gas utility company and a licensed contractor.
Once the gas line is in place, an HVAC technician will remove the electric furnace and install the gas furnace, connecting it to the newly established gas supply. The existing ductwork is typically reusable unless significant repairs or replacements are necessary.
Finally, the technician will ensure that the gas furnace is properly vented to safely expel combustion gases outside the home.
How Do You Light a Gas Furnace?
1. Turn Off the Gas
Always prioritize safety when working with heating systems. Before attempting to relight the pilot on your furnace, ensure the gas valve is turned off. You’ll typically find the valve near the furnace with a lever or switch that can be turned to the “off” position. If you detect the smell of gas or suspect a leak, evacuate the area immediately and contact a professional for assistance.
2. Locate the Pilot Light
After turning off the gas and confirming that safety measures are in place, locate the pilot light. It’s usually positioned near the base of the furnace. Look for an access panel, which may be labeled with instructions or a pilot symbol. Remove this panel to expose the pilot light assembly.
3. Allow Gas to Dissipate
Wait a few minutes to let any remaining gas dissipate from the area. This step is critical for safety to avoid gas buildup when you relight the pilot.
4. Set the Pilot Control Knob
After waiting, turn the pilot control knob to the “Pilot” position. Press and hold down the knob to allow gas to flow to the pilot light.
5. Light the Pilot
While holding the knob down, use a long lighter or match to ignite the pilot light at the end of the tube. Keep the knob pressed for about 30 seconds to ensure the flame remains lit. Afterward, release the knob. If the pilot light goes out, repeat the process, holding the knob down long enough for the thermocouple to warm up.
6. Switch the Knob to On
Once the pilot light is stable, turn the control knob to the “On” position. This will open the flow of gas to the main burner, allowing your furnace to start working again.
Choosing between an electric and gas furnace depends on several key factors: cost, efficiency, heating power, environmental impact, and climate suitability. Ultimately, homeowners should weigh their priorities—cost, energy efficiency, environmental impact, and regional climate—when deciding on the best furnace type for their needs, consulting a professional HVAC technician if needed to ensure an optimal choice.
No matter your decision, Santanna Energy Services can help you power your home with earth-friendly natural gas and electricity options, ensuring your energy choices align with your sustainability goals!
Tyler is an experienced energy professional, having worked for Santanna Energy Services, for the past four years. He is passionate about renewable energy and believes that diversifying the energy grid is the key to a sustainable future. Tyler is dedicated to supplying consumers with the best possible energy solutions and works diligently to make sure that Santanna can deliver the highest quality service.