Everything You Need to Know About Energy Deregulation
by Greg Rabaey
16.4 min read

Energy deregulation has revolutionized the way consumers access electricity and natural gas, offering more choice and control than ever before. By breaking up monopolies and opening the market to competition, deregulation has allowed households and businesses to select energy suppliers that best suit their needs. But what exactly does energy deregulation mean, and how does it impact you?
In this blog, we'll cover everything you need to know—from its benefits and challenges to tips for navigating deregulated markets—so you can make informed decisions about your energy options.
Key Points of This Article:
- Energy deregulation allows consumers to choose their electricity or natural gas supplier, creating competition that leads to better pricing, more plan options, and improved service.
- In regulated markets, a single government‑controlled utility manages all generation, delivery, and pricing, while deregulated markets separate supply from delivery to encourage competition.
- Deregulation benefits consumers by expanding choices, increasing transparency, enabling customized plans, and making it easier to switch providers without affecting service reliability.
- The shift toward deregulation has evolved over decades, varies by state, and continues to influence renewable energy growth, economic development, and consumer savings opportunities.
What Is Energy Deregulation? And Why It Matters
Does the choice of what you buy and who you buy it from matter to you?
In much the same way that you can choose between different grocery stores to shop the difference in prices, service, and products — energy and natural gas deregulation provides the ability to choose your gas or electricity provider. With choice comes the opportunity to select providers who can provide you with superior levels of service and allow you to choose different service options, such as:
- Fixed-rate solutions that offer consistent pricing even during unstable markets
- Electricity and natural gas services that are better for the earth
- Convenient unlimited plans where, just like a cell phone plan, you pay the same each month without having to worry about how much electricity or gas you use on a monthly basis.
If you’re living in — or will be moving to — a state that has deregulated energy or natural gas markets, here’s what you need to know about how these markets operate, and how the benefits provided by the deregulation of utilities affect the benefits available to you as a consumer.
How Does Energy Deregulation Work?
In a deregulated market, consumers can select their energy supplier based on factors like pricing, flexible energy plan options, and plan features. In these markets, utilities don't dictate energy rates and competition among suppliers is encouraged to drive better options for those seeking energy.
Energy suppliers compete by offering lower prices, customized plans, or value-added services such as Earth-Friendly energy options or rewards programs. This competition can lead to innovation and more tailored offerings for consumers.
Even with energy deregulation, your local utility company remains responsible for delivering energy to your property and maintaining infrastructure and handles billing. You receive one bill that combines charges for energy supply (from your chosen supplier) and delivery (from the utility).
Regulated vs Deregulated Energy Markets
In regulated markets, the government or a similar organization has complete oversight and control of providing goods and services. In a regulated energy or natural gas market, the government establishes a public utility company that is in charge of providing the power that operates the lighting, heating, air conditioning, electronics, and appliance operations for both businesses and residential consumers.
Public utilities are organizations established by the government and regulated by public utilities commissions for the purpose of providing “essential” services — such as water, electricity, gas, and communications. In a regulated market, the public utility may have monopoly rights over specific areas of the market or geographic locations — meaning they are the sole operators and there is no right for competition.
In a regulated electricity market, the public utility company owns and operates all electricity, from the generation to the meter, selling power directly to the customers. Similarly, in regulated gas markets, the government has sole oversight and control over the production and delivery of natural gas. The utility company also fully owns the infrastructure, transmission lines and pipelines and is responsible for their maintenance and operation as well as all new construction.
What is a regulated energy or natural gas market?
In regulated markets, the government or a similar organization has complete oversight and control of providing goods and services. In a regulated energy or natural gas market, the government establishes a public utility company that is in charge of providing the power that operates the lighting, heating, air conditioning, electronics, and appliance operations for both businesses and residential consumers.
Public utilities are organizations established by the government and regulated by public utilities commissions for the purpose of providing “essential” services — such as water, electricity, gas, and communications. In a regulated market, the public utility may have monopoly rights over specific areas of the market or geographic locations — meaning they are the sole operators and there is no right for competition.
In a regulated electricity market, the public utility company owns and operates all electricity, from the generation to the meter, selling power directly to the customers. Similarly, in regulated gas markets, the government has sole oversight and control over the production and delivery of natural gas. The utility company also fully owns the infrastructure, transmission lines and pipelines and is responsible for their maintenance and operation as well as all new construction.
What is a deregulated energy or natural gas market?
In a deregulated market, the government breaks up central control which allows multiple retail companies — also called third party energy service companies (ESCOs) — to compete against each other. The deregulated retail market allows different ESCOs to purchase energy at wholesale prices from providers and then sell to consumers. Because ESCOs have to compete for consumers, they’ll attempt to outperform other providers by offering better service, different energy options, or different price plans or contract structures.
In a deregulated gas market, retail gas suppliers purchase gas at the “wellhead” — where natural gas is extracted from a well — and arrange for its transportation to the local gas utility. How and where these gas marketers purchase natural gas can result in savings for consumers through a combination of lower wholesale costs, lower storage costs, and fewer state and local taxes.
Similarly, in a deregulated electricity market, retail providers will purchase electricity from different power plants. Depending on the type of power plant, the generated electricity may be considered “greener” or “earth-friendly” when it is from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric. Different ESCOs can also offer varying levels of service and available pricing plans — including fixed pricing, indexed pricing, and hybrid plans.
Even in a deregulated energy market, the local utilities still own and operate the infrastructure, transmission lines, and pipelines. In most cases, you’ll still receive and pay a single gas or electrical bill to your local utility company.
What are the benefits of regulated energy or natural gas?
The earliest days of energy services in the U.S. were largely unregulated, which proved challenging for providers and consumers alike. A lack of oversight led to exploitation of consumers, poorly managed and faulty infrastructure, a lack of access for rural and isolated communities, and the rise of private monopolies. In regulated markets, the government has complete control over the utilities and is required to work in the public’s interest. As a result, consumers in regulated energy markets tend to enjoy:
- Prices that tend to stay set and stable, with few spikes in cost
- Long-term stability and certainty they will have access to heat and electricity
- Continued oversight to prevent safety violations, abuse, or neglect
What are the benefits of deregulated energy and natural gas?
In practice, regulated markets suffered some of the same problems that unregulated markets did. No competition over price meant that consumers were stuck paying for whatever service was available, utilities weren’t incentivized to provide better service, and government monopolies proved as problematic as private ones. Deregulated energy markets solves these issues by introducing competition, and as a result, consumers can enjoy:
- Greater choice in options available — Being able to choose from different ESCOs allows consumers to shop around for options that are best for them.
- Improved customer service — Increased competition among energy providers motivates providers to offer better service to their customers.
- More transparency — Energy deregulation helps consumers understand where their energy and natural gas comes from and what it costs. Consumers can readily review their electricity and gas options and evaluate available energy plans.
- More choices in services — Competitive energy suppliers can offer additional services and benefits to their energy and natural gas customers, such as unlimited energy and gas options, or earth-friendly energy or gas options.
How Energy Deregulation Affects You as a Consumer
Energy deregulation puts the power in your hands by giving you choices when it comes to selecting your energy provider and plan. Here’s how it impacts you:
- Your Options Expand: You can shop around and compare energy suppliers to find a plan that fits your needs and lifestyle. Whether you’re looking for lower rates, to support renewable energy, or fixed pricing for protection against price hikes, most energy suppliers have these plan choices to fit your needs.
- Customized Plans: Deregulation often means more plan options, like renewable energy plans, time-of-use pricing, or rewards programs tailored to your preferences.
- Improved Service: Competition pushes suppliers to offer better customer service and innovative features to stand out in the market.
- Clear Billing: Even in a deregulated market, your local utility continues to handle delivery and infrastructure, so you still receive one simple bill that separates supply and delivery charges.
- Flexibility to Switch: If you’re not happy with your current provider, deregulation makes it easier to switch to another without affecting the reliability of your energy service.
What is the history of energy and natural gas deregulation?
The poor service and inconsistent pricing of the earliest energy and gas markets gouging weren’t the only problems consumers had to deal with. Because building and maintaining infrastructure is difficult and costly, some areas lacked power entirely because it wasn’t profitable enough for companies to build power lines or pipelines.
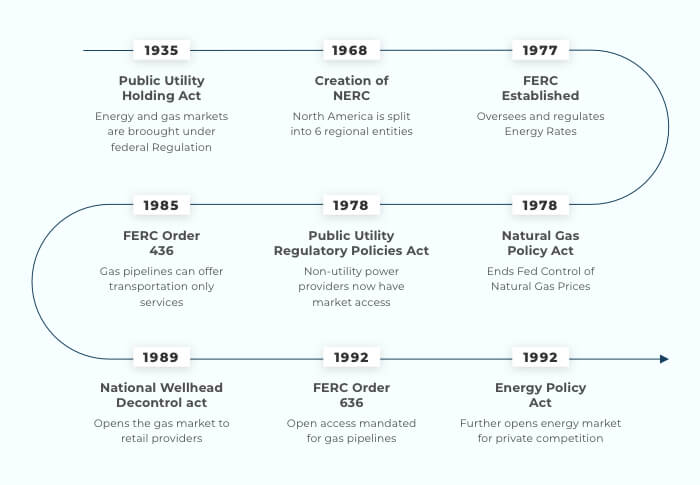
To reign in the energy market and set standards to better serve citizens, in 1935 the U.S. passed the Public Utility Holding Company Act (PUHCA) and then created the North American Electric Reliability Council (NERC) — now known as the North American Electric Reliability Corporation — in 1968. NERC split both the U.S. and Canada into 6 energy regions, with each region assuming responsibility for controlling energy and improving the reliability of energy delivery.
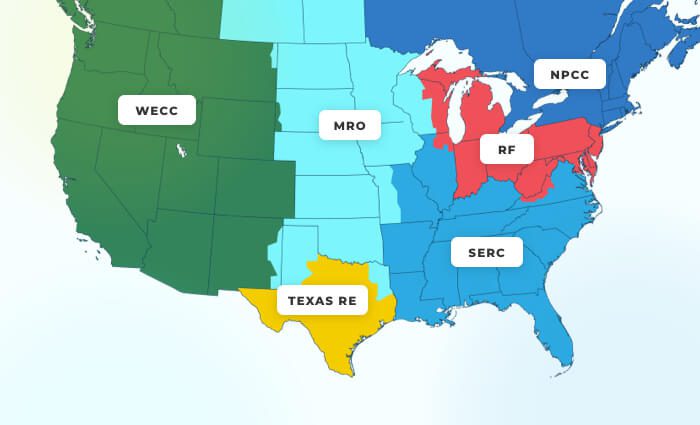
The six NERC Regional Entities are:
|
|
Regulation has its own set of challenges, such as state-owned monopolies and lack of options for consumers. These problems reached a breaking point during the oil embargoes of the 1970s, which brought record high gas and energy prices to all parts of the country. In response, the federal government created the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) in 1977 and then a year later, passed the Public Utilities Regulatory Policies Act, which left the question of how to supply energy up to individual states.
Prior to this, gas producers sold gas to interstate pipeline companies, which, in turn, sold it to local gas utilities, which then sold to end users such as residential customers and small businesses. The 1978 Natural Gas Policy Act ended federal control over the price of gas, starting the deregulation of the gas market and enabling different states to compete in purchasing gas and providing it to consumers.
In 1985, FERC issued Order 436 to further deregulate the gas market by allowing pipelines to offer transportation-only services for gas, which allowed some customers the ability to choose their gas provider. Then, in 1989, the Natural Gas Wellhead Decontrol Act removed federal price regulations, providing retail gas providers the ability to sell gas within an open market. The separation between transportation and purchase was further mandated in 1992 with FERC Order 636, creating truly “open access” pipelines for different gas providers to compete over.
The passing of the Energy Policy Act in 1992 allowed non-utility generators to have access to transmission networks and created the exempt wholesale market for electricity generators. This allowed for private competition and further energy deregulation of electricity markets in several states.
As of 2023, half of all U.S. states plus Washington D.C. offer some form of deregulated electricity and natural gas.
When Did Energy Deregulate?
Starting in the 1990s, several U.S. states began deregulating their electricity markets to encourage competition and reduce costs. This process, called restructuring, required traditional utility companies to sell off their power plants, leading to the rise of independent energy suppliers that owned the generators. Since building new power line systems for each supplier would be too expensive, utilities kept ownership of the transmission and distribution infrastructure. These utilities, now focused solely on delivering electricity, remain under regulation.
Timeline of Energy Deregulation within the United States
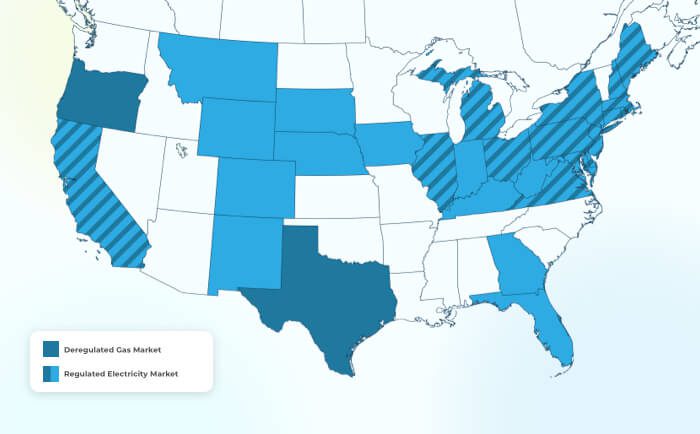
List of States with Deregulated Energy
The following states have deregulated electricity markets
|
|
|
The following states have deregulated gas markets
|
|
List of States with Regulated Energy
Five states in the U.S. aren’t considered fully deregulated and offer limited choices for electricity and/or gas: California, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, and West Virginia.
Twenty-four states across the nation are regulated markets and do not offer any forms of energy deregulation:
|
|
|
Impact of Deregulation on Renewable Energy
Energy deregulation encourages suppliers to offer renewable energy plans that utilize green energy sources such as solar and wind, giving consumers more choices to support sustainability.
Deregulation in the energy market also promotes competition and motivates energy suppliers to offer competitive rates and plans that may lead to potential savings while enrolled on a renewable energy plan. In the same way, customers might have access to Inflation Reduction Act’s Tax Incentives that are available in deregulated markets to fight climate change and grow the clean energy economy.
Because suppliers in deregulated states often offer green energy plans, deregulation can accelerates the shift from fossil fuels to cleaner energy sources by promoting innovation and competition. Because of this, consumers can choose suppliers that prioritize sustainability, helping drive demand for more environmentally friendly energy solutions.
Economic and Environmental Impacts of Deregulation
One of the most important benefits energy deregulation can bring to the economy is jobs! Deregulation fosters new opportunities for employment in renewable energy, energy technology, and competitive supply chains.
Energy deregulation also leads to increased competition which helps reduce prices, allowing for potential savings which can boost economic activity. Companies also compete to develop cutting-edge energy solutions, from smart grids to more efficient renewable energy technologies which boosts technological advances. Lastly, deregulation allows for the growth of new energy sectors, such as green energy and energy storage, contributing to a more diverse economy.
How To Find the Best Electricity Provider in a Deregulated Market
Choosing the right electricity provider in a deregulated market can potentially save you money and ensure your energy plan fits your needs and your lifestyle. Here’s what to consider when evaluating providers and contracts:
- Look for competitive rates and plan types such as fixed-rate, variable-rate, flat-fee (Unlimited Plans) or Earth-Friendly energy options.
- Carefully review the contract to understand the length, renewal terms, and any potential changes to rates after the initial term.
- Some providers charge fees if you decide to cancel your plan early. Ensure you’re comfortable with any penalties before signing.
- Research the provider’s reputation for customer service, trustworthiness and how long they’ve been in business.
- Some providers offer perks like rewards programs, energy usage tracking, or renewable energy options that align with your lifestyle as well as your values. Some local energy suppliers like Santanna Energy Services, donate to local charities in your area to give back to the community.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Energy Deregulation
How do I find out whether I live in an area with a deregulated market?
To determine if you reside in a deregulated energy market, consult your state’s public utility commission or official state government websites. These sources provide up-to-date information on energy market structures and consumer choices. Additionally, resources like the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) offer detailed maps and data on state energy regulations.
Does energy deregulation make energy more affordable?
Energy deregulation introduces competition among suppliers, which can lead to more competitive pricing and potentially lower energy costs for consumers. However, savings are not guaranteed and can vary based on factors like market conditions, geographic location, and individual usage patterns. It’s essential to compare rates and plans from different suppliers to identify potential savings.
Who controls power lines & gas pipelines?
In both regulated and deregulated markets, local utility companies are responsible for maintaining and operating the physical infrastructure, including power lines and gas pipelines. They ensure the safe and reliable delivery of energy to consumers, regardless of the energy supplier chosen. These utilities are typically regulated by state public utility commissions to ensure fair access and service quality.
Do I still contact my utility company during outages?
Yes, during power outages or emergencies, you should contact your local utility company. They are responsible for maintaining the infrastructure and restoring service, regardless of your energy supplier. Your utility’s contact information is usually found on your energy bill or their official website.
Are all states moving toward deregulation?
Not all states are moving toward energy deregulation. While some have embraced deregulation to promote competition and consumer choice, others have maintained regulated markets due to concerns about market stability, pricing, and infrastructure management. The status of energy deregulation varies by state, and some have even reversed or halted deregulation efforts after initial implementation.
How do I switch to a different energy provider?
To switch energy providers in a deregulated market:
- Research Providers: Compare rates, plans, and customer reviews of licensed energy suppliers in your area.
- Select a Plan: Choose a plan that fits your needs, considering factors like rate type (fixed, variable or flat), contract length, and any additional services.
- Review Contract Terms: Carefully read the contract for details on pricing, fees, and renewal terms.
- Enroll with the New Provider: Sign up for the chosen plan, providing necessary information such as your utility account number.
- Confirmation: Your new provider will coordinate with your utility to manage the switch, which typically occurs without service interruption.
- Monitor Your Bills: After the switch, review your bills to ensure accurate billing and the application of the new rates.
For the full process, visit our blog here!
Let Santanna Energy Provide Your Energy Solutions
If you’re a resident of Ohio, Illinois, Pennsylvania, Michigan, or Indiana, then you could be eligible to receive electricity and natural gas services from Santanna Energy Services. We offer fixed rates, unlimited energy plans, and renewable energy options. Plus, options for earth-friendly electricity and gas options.
Visit our site to check your zip code to see if you’re in our coverage area and view our available energy plans that are tailored to your lifestyle.
Greg Rabaey is the retired CEO of Santanna Energy Services and a respected leader with more than 30 years of experience spanning technology and the energy industry. With a strong academic background in mathematics, computer science, and physics, including a Ph.D. in Physics from the University of Arizona, Greg brought analytical rigor and forward-thinking leadership to every stage of his career.
During his tenure at Santanna Energy Services, Greg played a pivotal role in shaping the company into a consumer-centric energy provider, delivering electricity and natural gas to homes across the Midwest. His strategic vision, commitment to innovation, and dedication to both employees and customers helped drive the company’s growth and expand its earth-friendly and unlimited energy offerings.
Now retired, Greg remains proud of the foundation he helped build and the lasting impact of Santanna’s mission. Outside of his professional achievements, he is known for his strong commitment to community involvement and his belief in driving positive change through leadership, integrity, and service.