How Does Energy Pricing Work?
by Tyler Castle
21.5 min read

Energy pricing isn't just about the rate you pay—it's shaped by market demand, fuel costs, regulations, and grid infrastructure. Understanding these factors can help you avoid overpaying, lock in stable rates, and optimize your energy usage.
In this guide, we'll break down how energy prices are set, what influences them, and how to compare plans effectively. Knowing how energy pricing works will empower you to make smarter choices and save money. Read on to find out how to secure the best energy price for your needs!
Key Points of This Article:
- Understanding how energy pricing works helps households manage budgets, choose the right plan, and anticipate seasonal price changes.
- Electricity rates are shaped by generation costs, transmission and distribution expenses, market conditions, taxes, and government fees.
- Utilities offer regulated, relatively stable pricing, while suppliers in deregulated states provide flexible, market‑driven rates and more plan options.
- Energy prices rise due to factors like fuel costs, weather, infrastructure needs, global events, and supply‑and‑demand shifts, making efficiency and smart plan selection essential.
Why Understanding Energy Pricing Is Crucial for Residential Customers
Understanding energy pricing is essential for residential customers, as it directly impacts financial management, decision-making, energy efficiency, and the ability to navigate market fluctuations. Here's an expanded look at why this knowledge is crucial:
1. Financial Management
Energy expenses constitute a significant portion of household costs. By comprehending how energy pricing works, homeowners can anticipate and plan for these expenses more effectively.
In the same way, understanding rate structures and billing components enables consumers to adjust their usage patterns or invest in energy-efficient appliances, leading to reduced costs. This also helps customers understand why prices fluctuate so often and why they should lock in a good rate before seasons of high demand hit.
2. Informed Decision-Making
The knowledge of different pricing models—such as fixed-rate, variable-rate, and flat-fee plans—empowers consumers to select options that align with their usage habits and financial goals. In deregulated markets, understanding pricing helps consumers compare offers from various energy suppliers, ensuring they choose the best and most suitable option for their lifestyle.
3. Knowledge of Energy Conservation and Efficiency
Awareness of peak energy pricing periods encourages consumers to shift their energy use to off-peak times, leading to potential savings. Also, understanding how consumption affects pricing can motivate homeowners to invest in energy-efficient appliances or home improvements, reducing overall energy usage.
4. Power to Navigate Market Fluctuations
Knowledge of factors influencing energy prices, such as fuel costs and seasonal demand, helps consumers anticipate and respond to price fluctuations. Informed consumers are better equipped to engage in discussions about energy policies and advocate for fair pricing structures within their communities.

How Is Electricity Priced?
Many factors influence how electricity is priced. From supply and demand to transmission costs and government regulations, several elements come into play when determining how much you pay for power. Let's break down the key components that effect electricity pricing and the rate you pay:
1. Generation Costs
These costs are associated with producing electricity from various energy sources, including coal, natural gas, nuclear, and renewables like wind and solar. Factors influencing generation costs include fuel prices, operational expenses, maintenance, and the capital costs of constructing power plants. For instance, fluctuations in natural gas prices can significantly impact electricity generation costs, as natural gas is a common fuel for electric power plants.
2. Transmission and Distribution
Once electricity is generated, it must be transported from power plants to consumers. This involves high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution networks. Costs in this category cover the construction, maintenance, and operation of these networks, which affects the cost of electricity. Investments in infrastructure, repairs from weather-related damage, and upgrades to improve reliability and cybersecurity are included in these expenses.
3. Market Dynamics
Electricity prices are also subject to market dynamics such as supply and demand, fuel costs, and geopolitical events. During periods of high demand or fuel supply constraints, electricity prices may rise. Regulatory policies and environmental considerations can influence market dynamics and, consequently, electricity pricing.
4. Taxes and Additional Fees – Government Charges
Governments often impose taxes and surcharges on electricity bills to fund various public programs and infrastructure projects. These charges help support the development of new power plants, grid modernization, and energy infrastructure improvements, ensuring a reliable power supply.
Additionally, some of these fees go toward renewable energy initiatives, promoting clean energy sources like solar and wind power through incentives and subsidies. Public benefit programs are another key component, providing financial assistance for low-income households and funding energy efficiency projects aimed at reducing overall energy consumption. These taxes and fees vary by location and are usually listed as separate line items on electricity bills, influencing the total amount consumers pay.
What's the Pricing Difference: How Utilities and Suppliers Price Energy
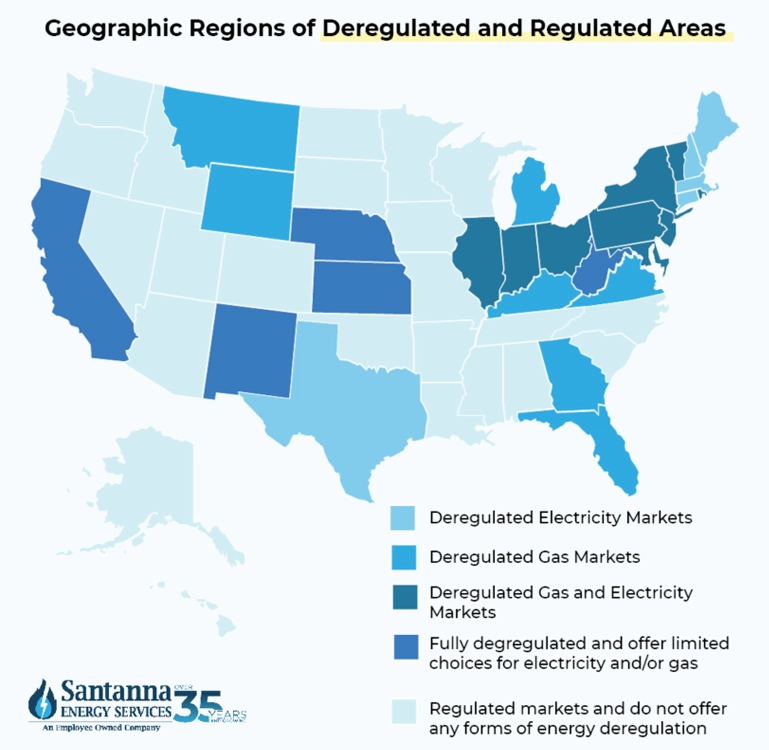
Understanding how utilities and energy suppliers set their prices can help consumers make informed choices on whether or not to sign up with their local utility or a supplier. It's important to note that not all states are eligible to sign up with a supplier as energy deregulation limits their choices.
Here's what you need to know about how utilities and energy suppliers' price their energy:
Utility Pricing: Stable but Regulated
Utilities operate under state regulations, ensuring some level of predictable pricing. Their Price to Compare (the rate they price their energy at) can be updated as little as twice a year or as often as monthly, depending on the utility.
Consumers can benefit from pricing stability signing up with utilities that don't adjust their rates frequently but may miss out on potential market-driven savings. Local utilities also have limited plan options to choose from making it hard for consumers to choose a plan that's right for their lifestyle.
Supplier Pricing: Market-Driven and Flexible
Retail energy suppliers operate in deregulated markets and adjust their rates based on real-time energy costs, fuel prices, and demand fluctuations. Unlike utilities, suppliers can change their prices daily, offering more flexibility and potential savings. They also provide diverse plan options, such as fixed-rate, variable-rate, and flat-fee plans so you can choose a plan that fits your energy habits and goals.
Again, keep in mind that only customers within deregulated states like Ohio, Illinois and Pennsylvania have the right to choose an energy supplier while states in regulated markets are often limited to only the local utility.
Factors That Influence Energy Price Increases
Energy prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors that can lead to fluctuations in consumer costs. Understanding these elements is crucial for both consumers and policymakers. Let's take a look at some of the most important factors that affect energy price increases:
1. Fuel Prices
The cost of fuels such as natural gas, coal, and oil significantly impacts electricity prices. When fuel prices rise, the expenses associated with generating electricity increase, leading to higher consumer prices. Global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and natural disasters can also drive fuel prices up.
2. Infrastructure Investments
Maintaining and upgrading energy infrastructure, including power plants and transmission lines, requires substantial investment. These costs are often passed on to consumers, resulting in increased electricity prices. Upgrades may include modernizing aging grids, expanding renewable energy capacity, or implementing smart grid technology to improve efficiency.
3. Environmental Policies
Regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy sources can affect energy production costs. Compliance with these policies may require additional investments, influencing consumer prices.
4. Weather Conditions
Extreme temperatures can increase demand for heating and cooling, leading to higher electricity consumption and prices. Additionally, weather events such as hurricanes, wildfires, and winter storms can disrupt energy supply chains, damage infrastructure, and limit fuel availability, all of which drive up costs. Droughts can also impact hydropower generation, reducing electricity supply and causing prices to rise in affected regions.
5. Global Events
International events, such as geopolitical conflicts or trade disputes, can disrupt energy supplies and influence prices. Tariffs on energy imports can lead to increased consumer costs.
6. Power Generation Availability
The availability of power generation sources, including renewable energy, affects electricity prices. Fluctuations in availability can lead to price changes. Unexpected outages at power plants, fuel supply disruptions, and seasonal variations in renewable energy output can lead to price fluctuations. For instance, wind and solar power generation depend on weather conditions, and when these sources underperform, utilities must rely on more expensive backup power sources.
7. Grid Distribution
The cost of maintaining and upgrading the energy grid directly affects pricing. When transmission lines are congested or require repairs, utilities pass these costs to consumers, increasing rates. Regions with outdated grids face higher distribution costs, making energy more expensive.
8. Consumer Supply and Demand
During peak seasons (summer for A/C, winter for heating), demand surges, forcing utilities to activate expensive power plants and buy additional energy at higher market rates. When demand is high, fuel prices rise, further driving up costs.
9. Power Supply Availability
Limited energy supply due to fuel shortages, extreme weather, or plant outages results in higher electricity prices. If renewables underperform due to low wind or cloudy days, utilities rely on higher-cost fossil fuels, pushing prices up.
10. Your Location
Where you live determines your access to energy sources and market regulations. Areas that import fuel or lack renewable infrastructure typically face higher energy costs. State taxes, regulations, and weather conditions also contribute to price differences.
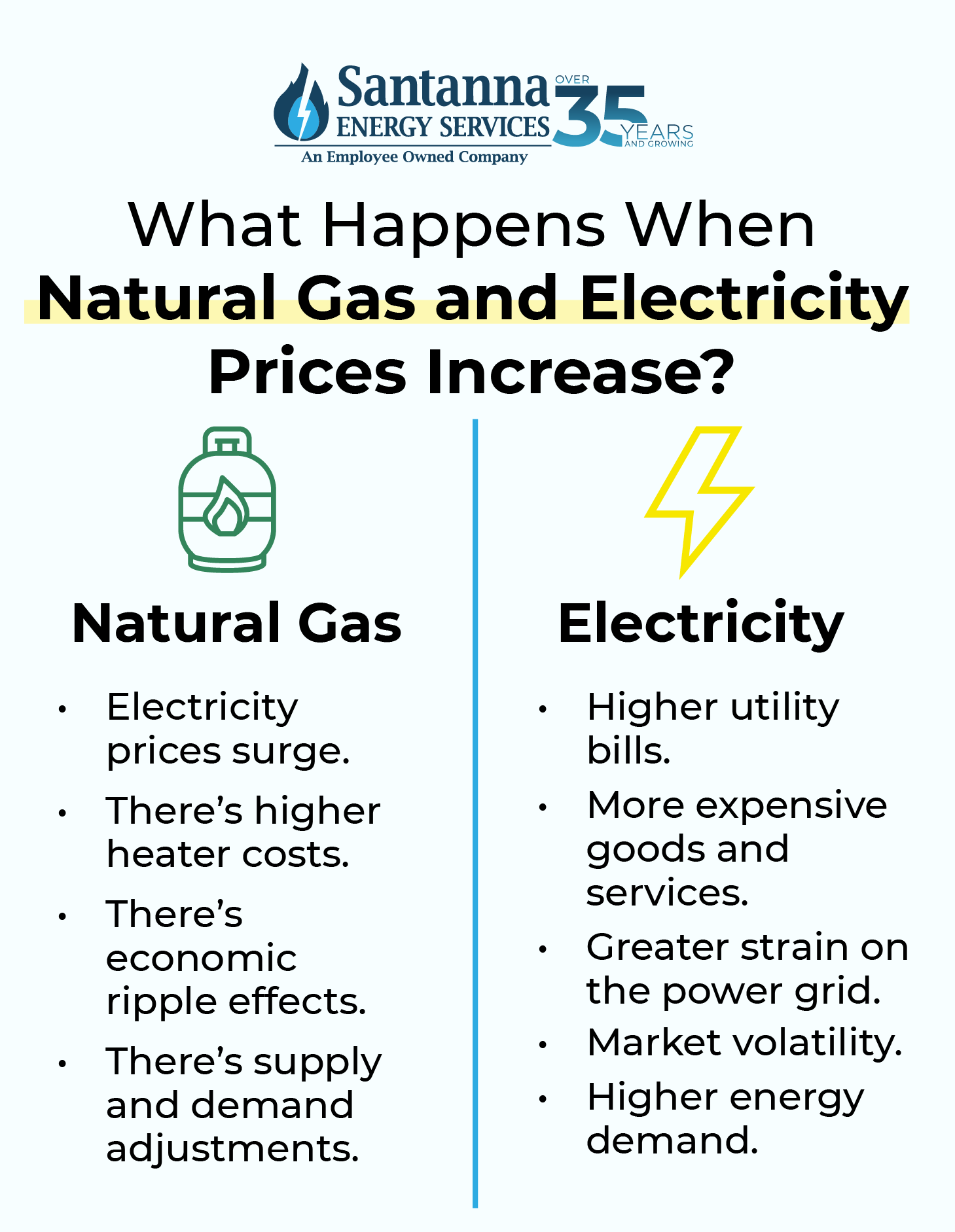
What Happens When the Price of Natural Gas Increases?
Natural gas plays a significant role in electricity generation, heating, and industrial production, making its price fluctuations a major driver of overall energy costs. When natural gas prices rise, the impacts are felt across households, businesses, and the economy. Here's why it happens and how to prepare:
1. Electricity Price Surges
Natural gas is a primary fuel source for power plants, especially in the U.S., where nearly 43% of electricity is generated using natural gas. A rise in natural gas prices directly increases electricity costs, leading to higher monthly bills for consumers.
2. Higher Heating Costs
Many homes rely on natural gas for heating, especially in cold-weather regions like the Amercian Midwest. When prices rise, winter heating bills can skyrocket, straining household budgets and increasing costs for businesses.
Prepare for these higher heating costs by investing in energy-efficient appliances and home insulation to reduce heating costs. Enroll in a fixed-rate energy plan that offers price certainty & stability even when market prices become volatile. Consider exploring dual-fuel heating systems that can switch between gas and electricity based on price fluctuations.
3. Economic Ripple Effects
Since natural gas is used in fuel production, rising prices can increase shipping and logistics costs, affecting prices of everyday goods. Sectors like chemical manufacturing, steel production, and food processing rely heavily on natural gas. Price hikes can reduce production, increase costs, and lead to job cuts and an increase in prices.
Prepare for these price changes by monitoring natural gas price trends through energy providers or market reports to anticipate cost changes.
4. Supply and Demand Adjustments
When prices rise, gas production often increases as companies ramp up drilling and imports to meet demand. Natural gas stored in underground reserves may be sold to balance prices, helping stabilize markets. If demand drops due to mild weather or efficiency improvements, prices tend to decline, reducing overall costs.
Be aware of market cycles—if gas prices are high now, they may decline in the near future as supply catches up. Households can invest in smart thermostats and energy-saving practices to lessen gas consumption.
Rising natural gas prices have far-reaching effects on electricity, heating, and the overall economy. By choosing the right energy plan, improving efficiency, and staying informed, consumers and businesses can better manage their energy costs and reduce financial strain during price hikes.
What Happens When Electricity Prices Increase?
When electricity prices rise, the impact is felt across households, businesses, and the economy. Below are the key events that occur when energy costs increase, along with practical ways to prepare and minimize financial strain.
- Higher Utility Bills: As electricity rates climb, households and businesses pay more for the same amount of energy, leading to budget constraints and financial stress. Prepare for these higher bills by reducing energy consumption by switching to LED lighting, smart thermostats, and energy-efficient appliances.
- More Expensive Goods & Services: Rising energy costs could affect goods and services and have tracked along with the rate of inflation in recent years. This leads to higher prices on food, fuel, and everyday essentials. Be sure to monitor household budgets and adjust discretionary spending to prioritize essential needs. Take advantage of energy-efficient rebates and government assistance programs that offer discounts on utility costs.
- Greater Strain on the Power Grid: High demand—especially during summer heat waves or winter storms—puts stress on the power grid, increasing the likelihood of blackouts or brownouts.
- Market Volatility & Pricing Uncertainty: Energy prices fluctuate based on fuel shortages, supply chain disruptions, and global economic conditions, making it difficult to predict long-term costs. Increased demand often leads to higher electricity prices leaving people on energy plans that are vulnerable to market fluctuations (like variable-rate plans) to pay more. To prepare, stay ahead of pricing trends by comparing supplier rates and opting for long-term energy contracts and review your electricity plan annually to ensure you're on the most cost-effective option.
- Higher Demand for Energy Assistance Programs: Low-income households may struggle to afford rising electricity bills, increasing demand for government and nonprofit assistance programs. Prepare by checking if you qualify for federal, state, or local energy assistance programs
Electricity price increases are inevitable, but taking proactive steps today can reduce their financial impact. Locking into an Unlimited Energy Plan where your supply charge never changes, improving energy efficiency, and considering renewable energy options can provide peace of mind and protection from price spikes all year long!
Why Are Electricity Prices Highest in the Summer?
Electricity prices often peak during the summer months primarily due to increased demand for air conditioning as temperatures rise. This heightened demand requires utilities to activate additional power plants, often relying on more expensive and less efficient energy sources, leading to higher wholesale electricity prices. The immediate nature of electricity consumption—where supply must match demand in real-time—means that any surge in usage can swiftly drive up prices.
Why Are Natural Gas Prices Highest in the Winter?
Natural gas prices typically reach their highest levels in the winter. During this season, colder temperatures significantly increase the need for heating in residential and commercial buildings, leading to a substantial rise in natural gas consumption. This surge in demand can strain supply, especially if storage levels are not adequately maintained, resulting in elevated prices.
How Does Supply and Demand Affect Pricing?
Energy pricing is fundamentally driven by supply and demand dynamics, just like any other commodity. When demand increases or supply is disrupted, prices tend to rise. Conversely, when supply is abundant and demand is low, prices can decrease. Here's a deeper look at how these forces interact in the energy market:
During high-demand periods (summer heat waves, winter cold snaps), electricity usage spikes due to air conditioning and heating needs, causing wholesale electricity prices to increase. Off-peak hours (late night and early morning) often see lower demand, leading to reduced energy costs for suppliers. In the same way, increased air conditioning use leads to higher electricity consumption, driving up market prices. Heating requirements (especially in regions using natural gas) create supply constraints, causing natural gas and electricity prices to rise.
Energy generation depends on fuel sources like natural gas, coal, nuclear, hydro, wind, and solar. If fuel supply is limited due to geopolitical issues, infrastructure failures, or extreme weather, electricity prices increase. Natural gas prices heavily influence electricity costs, as many power plants rely on gas for generation. Supply shortages drive higher energy costs across the grid.
Lastly, energy transmission limitations (like congested power lines or aging infrastructure) can bottleneck supply, increasing costs even when generation capacity is sufficient. Regions with limited grid interconnections may experience higher volatility in pricing compared to areas with a strong, interconnected power grid.
How This Affects You as a Consumer
If demand is high, electricity bills tend to rise during peak seasons, making it important for consumers to plan accordingly. One way to manage costs is by locking in an energy plan, which provides price stability and protects against sudden rate increases.
Investing in energy efficiency measures, such as smart thermostats, improved insulation, or LED lighting, can further reduce overall consumption, leading to long-term savings on electricity bills.
How Your Location Affects Energy Pricing
In a regulated market, utilities often control the majority of the energy market and are responsible for both generating and delivering electricity to consumers. Prices are set by state regulators, and consumers cannot choose their supplier—they must buy directly from the utility.
In regulated markets, prices are typically more stable because utilities adjust rates only with regulatory approval (often once a month). In this market, consumers don't have access to competitive supplier rates, meaning there are fewer options for savings.
In deregulated markets, consumers have the freedom to choose their electricity supplier, while utilities continue to manage delivery and infrastructure. This fosters competition, often leading to lower rates and diverse plan options.
More competition means potential cost savings for consumers. And with more competition, suppliers often have better customer services, rewards programs, and monthly incentives to keep your business. Supplier pricing can fluctuate more frequently (sometimes daily), while utilities still charge separately for delivery costs.
What Types of Residential Energy Pricing Structures Are Available?
Choosing the right electricity pricing structure can significantly impact your monthly energy costs and how you manage your consumption. Here's a deep dive into the different types of residential energy pricing structures, their advantages, and considerations:
1. Fixed-Rate Plans: Lock In Your Rate
You lock in a fixed price per kWh for electricity and per therm for natural gas for the duration of your contract (usually 3 months to 2 years). Your rate remains the same regardless of market fluctuations, seasonal demand, or energy crises.
With this plan, you'll have a consistent energy rate which offers protection from market volatility—if energy prices rise, your rate stays the same. This pricing structure is best for long-term homeowners.
Some drawbacks of a fixed-rate pricing structure include missing out on cost savings when energy prices drop since you're locked into a contract. Some contracts have early termination fees, making it harder to switch plans and this plan isn't ideal for short-term renters or people planning to move soon.
2. Variable Rate Plan: Prices Change with Market Fluctuations
A variable-rate energy plan means that the price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) or therm fluctuates based on market conditions. Prices may rise or fall depending on fuel costs, seasonal demand, and energy supply availability.
On this plan, if market prices drop, you pay less for electricity or natural gas compared to a fixed-rate plan. These plans often do not require contracts, allowing flexibility to switch providers. Variable rate plans are ideal for renters or homeowners who don't want to be locked into a contract.
Be aware that if you are on a variable rate plan, rates can increase unexpectedly, making budgeting difficult. During summer and winter, demand surges may lead to significantly higher costs leading to high and frustrating bills.
This plan is best for consumers who actively monitor market trends and can adjust their energy usage accordingly. It's also a good choice for renters or short-term residents who don't want long-term contracts.
3. Flat-Fee or Unlimited Energy Plan: Same Supply Charge Each Month
A flat-fee or Unlimited Energy plan charges a fixed monthly supply charge regardless of how much electricity or natural gas you use. It protects your peace of mind since you pay the same supply charge each month, regardless of fluctuations in usage.*
As a pro of this plan, your supply charge stays the same, making it easier to manage finances. No feel no impact from seasonal demand or fuel cost fluctuations on your supply change when the market gets tough. Keep in mind that some energy providers do not offer this pricing model, limiting availability.
This plan is ideal for those who prefer billing predictability and who don't want to calculate their estimated bill based on usage each month and households who set a monthly budget.
Which Energy Pricing Structure Is Right for You?
| Plan Type | Best For | Key Benefit | Potential Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Rate Plan | Homeowners who want stable pricing | Consistent rate throughout contract | No savings when market prices drop |
| Variable-Rate Plan | Flexible consumers looking for market-driven savings | Possible lower rates in some months | Rates may spike unpredictably |
| Unlimited Energy Plan | Those who want predictability or who need to set a monthly budget | Predictable monthly supply charge | May pay more during low-usage periods |
How Are Charges Broken Down on My Energy Bill?
When you receive your energy bill, it includes charges from both your energy supplier and your local utility company. While your supplier determines the cost of the electricity or natural gas you use, your utility remains responsible for delivering that energy to your home or business—even if you choose a different supplier. Here's how these charges break down:
Charges Determined Specifically by Your Energy Supplier
The energy supply charge is the rate you pay per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity or per therm of natural gas. This competitive rate is set by your retail energy supplier, not your utility company. Your total energy charge depends on your consumption during the billing period and the pricing structure of your plan—whether it's fixed-rate, variable-rate, or time-of-use pricing.
If you switch to a retail energy supplier, your utility will still handle billing, but the supply portion of your bill will reflect your supplier's rate instead of the default utility rate.
Charges Determined Specifically by Your Local Utility Company
Regardless of who supplies your energy, your local utility is responsible for delivering electricity or natural gas to your location. Utility delivery charges cover the cost of maintaining power lines, pipelines, transformers, and substations that ensure energy reaches homes and businesses safely and reliably. These fees remain the same whether you purchase energy from the utility or an independent supplier.
These charges ensure that your energy can be reliably transmitted, regardless of which supplier you choose.
Capacity charges apply only to business customers and are designed to ensure the utility has enough available power to meet peak energy demand. This fee helps maintain grid stability and ensures that businesses have sufficient energy supply, even during high-demand periods.
Even if a business doesn't always use its maximum energy capacity, it must still pay for the reserved electricity capacity to avoid shortages.
Unlike capacity charges, demand charges are based on your actual energy consumption during peak usage periods. These charges fluctuate depending on when and how you use energy, particularly during high-demand seasons like hot summers or cold winters when energy usage spikes. Businesses that consume large amounts of electricity at once (such as manufacturing plants or large commercial buildings) typically see higher demand charges.
Reducing energy usage during peak hours can lower demand charges and reduce overall electricity costs.
How Can I Calculate My Total Energy Usage and Costs?
Calculating your total energy usage and associated costs is essential for effective household budgeting and implementing energy-saving measures. Here's how you can assess and manage your energy consumption:
1. Conduct an Energy Audit
A professional energy audit provides a comprehensive analysis of your home's energy use, identifying inefficiencies and recommending improvements. This process can uncover issues like poor insulation or outdated appliances that may be increasing your energy bills. Many utility companies offer energy audits or can recommend certified auditors.
2. Utilize Smart Meters
Installing smart meters allows you to monitor real-time energy consumption, offering insights into how and when you use energy. This data can help you adjust usage patterns to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Some utilities provide smart meters at no additional charge, so inquire with your provider about availability.
3. Review Utility Bills Regularly
Your utility bills contain valuable information about your energy usage over time. By examining these statements, you can identify trends, seasonal variations, and the impact of any energy-saving measures you've implemented. Comparing bills month-to-month or year-to-year can highlight areas where further improvements are possible.
4. Calculate Individual Appliance Consumption
Understanding how much energy each appliance uses can pinpoint opportunities for savings. Here's a method to estimate appliance energy consumption:
- Identify Wattage: Find the appliance's wattage, typically listed on a label or in the user manual.
- Estimate Daily Usage: Determine how many hours per day you use the appliance.
- Calculate Daily Energy Use: Multiply the wattage by the number of hours used daily, then divide by 1,000 to convert to kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Determine Monthly Consumption: Multiply the daily kWh usage by 30 (days) or however often you plan on using this appliance.
- Calculate Monthly Cost: Multiply the monthly kWh consumption by your utility's rate per kWh.
Choosing the best energy plan is not just about finding the lowest rate—it's about understanding how energy pricing works, anticipating market changes, and selecting a plan that aligns with your usage habits and financial goals.
At Santanna Energy Services, we provide competitive energy plans designed to help you manage costs effectively while offering renewable energy solutions for a cleaner, more sustainable future. Whether you need fixed-rate stability, earth-friendly energy options, or strategies to optimize your energy usage, we're here to help. Ready to take control of your energy? Explore our plans today!
* Restrictions apply. Enrollment based upon program eligibility. Customers using more than 125% of normal monthly usage as determined by Santanna may be required to switch plans.
Tyler is an experienced energy professional, having worked for Santanna Energy Services, for the past four years. He is passionate about renewable energy and believes that diversifying the energy grid is the key to a sustainable future. Tyler is dedicated to supplying consumers with the best possible energy solutions and works diligently to make sure that Santanna can deliver the highest quality service.