How Many Watts Does a TV Use? TV Electricity Usage & More
by Tyler Castle
14.7 min read

TVs are an integral part of most homes, contributing significantly to everyday entertainment and relaxation. With the rise of streaming and higher-resolution televisions, the average TV usage time is increasing. Whether you’re interested in lowering your electricity bill, choosing an energy-efficient TV, or simply understanding what contributes to your energy usage, this guide will break down everything you need to know about how many watts your TV consumes and how it affects your electricity costs.
Key Points of This Article:
- Modern TVs typically use around 100 watts, with actual wattage varying by screen size, technology, and settings.
- You can determine your TV’s wattage by checking the Energy Guide label, using an energy monitor, or calculating watts from volts and amps.
- TV electricity use depends on factors such as screen size, resolution, brightness, age, and display type, and larger or older models generally consume more power.
- Understanding wattage helps estimate energy costs and identify ways to reduce usage, including adjusting settings, enabling eco modes, and minimizing standby power.
What is the difference between watts and electricity consumption?
A watt is the unit of electrical power equal to one ampere under the pressure of one volt. This refers to the total amount of electrical energy used over time, usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). It represents the instantaneous power demand of an electrical device.
One kilowatt-hour is equivalent to using 1,000 watts of power for one hour. For instance, if a 100-watt TV is used for 10 hours, it consumes 1 kWh of electricity.
In short, watts measure the power at a specific moment, while electricity consumption (measured in kWh) indicates the total energy used over time.
How many watts does a TV use?
On average, modern TVs use around 100 watts, depending on the model. Larger screens require as much as 200 watts. TVs consume less electricity than your most energy-intensive appliances, but if you have multiple TVs in frequent use or larger screens, the energy consumption can add up fast.
Figuring out how many watts your TV uses depends on your TV’s size and TV type. Larger TVs use more watts than smaller ones, but modern energy-efficient models (like ENERGY STAR certified) help reduce overall consumption.
Average TV Wattage by Screen Size*
| TV Size (Inches) | Average Wattage (W) Per Hour |
|---|---|
| 23.53 inch – 31.6 inch | 23 – 31 |
| 32 inch – 42.5 inch | 34 – 64 |
| 47.5 inch – 50 inch | 66 – 70 |
| 54.5 inch – 57.5 inch | 83 – 104 |
| 64.5 inch – 65 inch | 112- 120 |
| 74.5 inch 85.6-inch | 125 – 184 |
*TV sizes and estimated watts taken from EnergyStar.com based on one hour of watch time. Watts can vary based on TV settings, watch time and type.
How to find your TV’s wattage
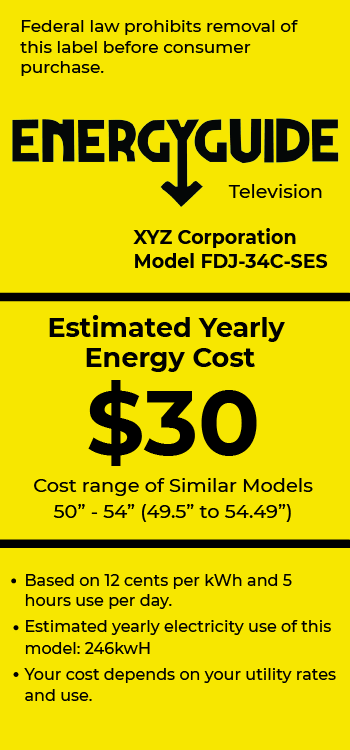
If you’re looking to figure out how many watts your TV uses, one of the most reliable and straightforward ways to determine your TV’s wattage is by checking the Energy Guide sticker, which is typically placed on the back of the TV or included in the product’s manual.
This label provides essential information, including:
- Estimated yearly energy cost.
- A visual scale showing how the TV’s energy cost or consumption compares to other similar-sized models.
- Information on the brand, specific model, and wattage to ensure you’re looking at the correct label for the product.
Here’s an example:
Energy Guide stickers give you an estimate of how much energy the TV consumes in a typical year, which helps you understand the overall efficiency. Some labels will list the power consumption in watts. If not, you can calculate it by multiplying the energy usage (kWh) by the number of hours you plan to use the TV.
Energy Guide labels often include an estimated cost of running the TV per year, based on national average electricity rates. This can be a useful reference point for budgeting your energy consumption.
If the Energy Guide sticker is not available or you want to track real-time energy usage, an energy monitor is an excellent alternative. These devices plug into your TV’s power outlet and measure the actual power consumption during use.
If you’re still unsure how you can find out how many watts your TV uses, search you model on your TV brand’s website. You can often find your TV’s wattage in the “specs” section of the TV’s information, listed under “wattage” or “power consumption”.
Knowing the volts and amps of your TV can help you calculate how many watts your TV uses
TVs operate on electrical power measured in volts (V) and amps (A). Volts indicate the electrical pressure or potential difference, while amps measure the flow of electricity. Knowing both values allows you to understand how much electricity your TV uses.
If you know how many volts and amps your TV consumes, you can easily calculate how many watts your TV uses. To find the wattage of your TV when all you have is your volts and amps, you can use the formula: Watts = Volts × Amps.
For example, if a TV runs on 120 volts and uses 1.5 amps, the wattage is 180 watts. This calculation helps you determine the actual energy usage of your TV.
How many watts does a TV use per hour?
The number of watts a TV uses per hour can vary significantly depending on the type, size and age of the TV. 32-inch LED TV typically uses about 30-60 watts per hour. 55-inch LED TV generally uses around 83-104 watts per hour, depending on the brightness settings and features.
Factors that Affect Your TV Wattage
- Screen size: Larger TVs generally consume more power and have an increase in TV wattage.
- Resolution: Higher resolutions (4K vs HD) require more processing power and can increase the TV’s electricity consumption compared to HD content. This is due to the extra processing needed for better image quality.
- TV type: Different screen technologies (LED, OLED, etc.) have different energy demands which can require higher wattages.
- Settings: Brightness levels, standby mode, and additional features can increase energy consumption.
- Age: Older TVs may consume more power than newer models due to outdated technology and less efficient components. Advances in energy-saving technology have made newer TVs generally more energy-efficient.
How many watts does a Samsung TV use?
How many watts your Samsung TV uses depends on your TV size, settings, display technology, and the type of content being displayed.
We’ve pulled three of the most common Samsung TV types from their online store and compiled a range of their most common model sizes and their wattage. Here’s how many watts a Samsung TV uses:
- QLED Samsung TV’s range from 55-85 inches and consume 140 – 209 watts.
- Typical OLED Samsung TV’s range from 55-77 inches and consume 129– 192 watts.
- UHD Samsung TV’s range from 43-85 inches and consume 56– 237 watts.
At the U.S. national average electricity rate of $0.1662 per kWh (as of July 2024), watching your Samsung TV for 5 hours a day could cost you about $1.39 to $5.90 per month, depending on the TV’s size and type.
These estimates are based on wattage data from Samsung’s TV inventory as of October 2024.
Samsung TV’s wattage compared to other TV brands
According to Sony’s online store, their TV models range from 43-85 inches and can consume anywhere from 103 – 372 watts. This of course varies depending on the type of TV you choose.
Vizio carries TV sizes from 20-86 inches that consume anywhere from 75 – 240 watts. This estimation varies depending on the type of TV you choose.
As you can see, the wattage of a Samsung TV varies significantly based on the model, screen size, and technology. When compared to other brands like Sony and Vizio, Samsung TVs tend to offer a range of power consumption that can meet different energy efficiency preferences.
If minimizing electricity costs is a priority, consider opting for a smaller screen size, adjusting the TV’s settings to lower brightness, or choosing energy-efficient display technology like QLED or OLED.
No matter which brand or type of TV you choose, making energy-conscious decisions, such as enabling energy-saving modes or using a smart power strip to eliminate standby power, can help reduce electricity consumption further.
How many watts a TV uses compared to other appliances in your home
| Appliance | Average Wattage (W) |
|---|---|
| Television (LED, 54.4-inch – 57.5 inch) | 83-104 |
| Refrigerator | 150-400 |
| Microwave | 600 – 1,700 |
| Dishwasher | 1,200 – 1,800 |
| Central Air Conditioner | 3,000 – 5,000 |
| Space Heater | 750 – 1,500 |
| Laptop | 50 – 100 |
How much electricity does a TV use?
Understanding how much electricity your TV uses is essential for several reasons, primarily tied to your energy bills, environmental impact, and efficiency. On average, modern TVs use around 100 watts, which equals 15 kWh of electricity in a month if watched for 5 hours each day.
Televisions can contribute significantly to your household electricity bill, especially if you have larger models, multiple TVs, or tend to keep the TV on for long periods. Knowing how much electricity your TV uses allows you to:
- Estimate Monthly and Yearly Costs: By calculating the wattage and your electricity rate, you can better manage your energy budget and avoid surprises.
- Identify Potential Savings: You can take steps to reduce unnecessary energy use by adjusting settings (e.g., brightness, resolution) or opting for a more energy-efficient model.
Electricity Usage Breakdown
How much electricity your TV uses depends on the wattage and the hours the TV is in use. Assuming you watch TV for 5 hours a day, you can expect your TV to consume…
How much electricity your TV uses by size, type, and watts
| Type of TV | Screen Size
(inches) |
Watts | Hours | Daily Kilowatt-hour (kWh)
consumption |
| LED | 32” | 40 | 5 | 0.2 |
| 40” | 70 | 5 | 0.35 | |
| 55” | 100 | 5 | 0.5 | |
| LCD TV | 32” | 45 | 5 | 0.225 |
| 40” | 75 | 5 | 0.375 | |
| 55” | 85 | 5 | 0.425 | |
| OLED | 32” | 55 | 5 | 0.275 |
| 40” | 65 | 5 | 0.325 | |
| 55” | 110 | 5 | 0.55 | |
| CRT | 32” | 150 | 5 | 0.75 |
| Plasma | 32” | 200 | 5 | 1 |
| 40” | 250 | 5 | 1.25 | |
| 55” | 280 | 5 | 1.4 |
TV types and how they affect how much electricity your TV uses
The type of television you own greatly affects your TV’s energy consumption. Let’s take a look at some of the most common TV types and how they play a role in TV wattage and your overall energy consumption:
- LED TVs: These are the most common TV sets found in homes. LED TVs offer more energy savings because of their light-emitting diode (LED) backlighting, which requires less power than traditional televisions and produces less heat.
- LCD TVs: These TVs use cold cathode fluorescent lamps for backlighting. LCD consume and require more electricity than LED TVs but are still more energy efficient than older models of plasma screen TVs.
- OLED TVs: Unlike LCDs, which rely on a backlight, OLED (organic light-emitting diode) TVs generate light individually in each pixel. OLED TVs generally use less power when displaying darker scenes but can consume more electricity when showing bright or high-contrast images
- CRT TVs: Think of your grandparent’s TV for this example. These older and bulkier TVs are extremely inefficient and consume more electricity compared to other TV alternatives.
- Plasma TVs: Plasma TVs are known for their vibrant colors and deep contrast, but they are more energy-intensive compared to LED and OLED models. They also produce more heat, which can further contribute to energy costs.
How to calculate the energy consumption of your TV
If you want to calculate how much energy your TV uses, there’s a simple formula to find out.
(Wattage × Hours Used Per Day) ÷ 1000 = Daily Kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumption
To find the annual energy consumption use the following formula:
Daily kWh consumption × number of days used per year = annual energy consumption
To find the annual cost to run the appliance use the following formula:
Annual energy consumption × utility rate per kWh = annual cost to run appliance
How much electricity does a TV use per month, day, week, & year?
Let’s say you own a 55-inch LED TV that uses 100 watts of electricity and you watch your TV for 5 hours per day. With all these factors in mind, your TV would consume 0.5 kWh per day, 3.5 kWh per week, 15 kWh per month, and 182.5 kWh per year.
To find out how much this will cost you, let’s assume your electricity costs $0.1722 per kWh, the U.S. national average as of March 2025. With all these factors considered, this is how much electricity your TV uses per hour, week, month, and year and how much it’ll cost you:
How Much Electricity a TV Uses Per Hour, Day, Week, Month & Year
| Time Period | Hours Used | Electricity Used (kWh) | Cost ($0.1711 per kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Per Hour | 1 | 0.1 | $0.0171 |
| Per Day | 5 | 0.5 | $0.0856 |
| Per Week | 35 | 3.5 | $0.989 |
| Per Month | 150 | 15 | $2.56 |
| Per Year | 1,825 | 182.5 | $31.26 |
How much electricity a TV uses by state
All charts are based on a usage of 5 hours per day at different wattages.
Daily Electricity Cost of a TV by State
| Wattage (W) | Pennsylvania ($0.1843/kWh)* | Illinois ($0.1759/kWh)* | Ohio ($0.1652/kWh)* | Michigan ($0.1937/kWh)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | $0.0645 | $0.0616 | $0.0578 | $0.0678 |
| 100 | $0.0922 | $0.0879 | $0.0826 | $0.0969 |
| 110 | $0.1014 | $0.0967 | $0.0908 | $0.1066 |
| 150 | $0.1383 | $0.1319 | $0.1239 | $0.1454 |
| 200 | $0.1843 | $0.1759 | $0.1652 | $0.1937 |
Weekly Electricity Cost of a TV by State
| Wattage (W) | Pennsylvania ($0.1843/kWh)* | Illinois ($0.1759/kWh)* | Ohio ($0.1652/kWh)* | Michigan ($0.1937/kWh)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | $0.45 | $0.43 | $0.40 | $0.47 |
| 100 | $0.64 | $0.62 | $0.58 | $0.68 |
| 110 | $0.71 | $0.68 | $0.64 | $0.75 |
| 150 | $0.97 | $0.92 | $0.87 | $1.02 |
| 200 | $1.29 | $1.23 | $1.16 | $1.36 |
Yearly Electricity Cost of a TV by State
| Wattage (W) | Pennsylvania ($0.1843/kWh)* | Illinois ($0.1759/kWh)* | Ohio ($0.1652/kWh)* | Michigan ($0.1937/kWh)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | $23.54 | $22.47 | $21.10 | $24.75 |
| 100 | $33.61 | $32.10 | $30.14 | $35.36 |
| 110 | $37.00 | $35.31 | $33.15 | $38.89 |
| 150 | $50.42 | $48.15 | $45.21 | $53.04 |
| 200 | $67.21 | $64.20 | $60.28 | $70.72 |
*Electricity rates are based on the state’s average electricity rate from the E.I.A as of March 2025
How much electricity a TV uses compared to other appliances in your home per year
Yearly Electricity Consumption Comparison of a TV to Common Appliances in Your Home
| Appliance | Power (Watts) | Usage (Hours/day) | Yearly Consumption (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TV | 100 | 5 | 182.5 |
| Refrigerator | 150 | 24 | 1,314 |
| Microwave | 1,000 | 1 | 365.0 |
| Dishwasher | 1,200 | 1 | 438.0 |
| Laptop | 60 | 8 | 175.2 |
Factors that affect the electricity consumption of a TV
Several factors influence how much electricity your TV uses, ranging from the size and technology to your viewing habits. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements that affect TV power consumption:
- Screen Size Larger TVs typically use more power than smaller ones due to the larger screen area that needs to be illuminated. For example, a 32-inch TV consumes less energy than a 65-inch TV, even if they use similar technology.
- Display Technology: Generally, LED and liquid crystal display (LCD) TVs are the most energy-efficient technology. LED and LCD TVs use less power compared to older technologies.
- Resolution: 4K/Ultra HD TVs consume 30% more power than standard HD TVs due to the higher processing demands and the need for better picture clarity. Streaming content in 8K further increases energy consumption compared to lower resolutions.
- Brightness Settings: High brightness settings significantly increase power usage. Reducing brightness or switching to eco modes can lead to lower energy consumption.
- Features like voice assistants and automatic updates running in the background can contribute to higher energy use.
- Standby Mode and Phantom Power: TVs still draw a small amount of power (phantom load) even when turned off but plugged in. This can add up over time, especially if you leave your TV in standby mode for long periods.
How much electricity does a TV use when off?
Even when turned off, a TV can still draw 1-2 watts of power if it’s plugged in, known as phantom load. Phantom load, also known as standby power, refers to the power gadgets waste just by being plugged in.
At the average electricity rate in the U.S. costs $0.1662 per kWh, the U.S. national average, a TV that’s turned off can waste $0.06 a week, $0.24 a month, and $2.91 a year! Multiple this by multiple TV units in your home, leaving your TV on standby mode or plugged in can really add up.
Does leaving the TV on waste electricity?
Yes, leaving the TV on does waste electricity! When a TV is turned on, it continues to draw power, even if you’re not actively watching it. The amount of electricity wasted depends on the TV’s power consumption rating.
Energy-saving tips to reduce TV power consumption
- Lower Brightness: Reducing the brightness can save energy, especially if the TV is set to high levels by default.
- Turn Off When Not in Use: Avoid leaving the TV on when no one is watching.
- Use Smart Plugs: These devices can help cut off electricity completely when the TV is in standby mode.
- Eco Modes: Enable energy-saving features like eco modes on your TV to automatically reduce power consumption.
- Reduce Screen Timeout: Set a shorter timeout period for the screen to turn off when inactive, which can help save energy.
- Unplug During Extended Absences: If you won’t be using the TV for an extended period, unplug it to prevent any energy draw from standby mode.
- Limit Streaming Quality: Lower the streaming quality on apps, as higher resolutions often consume more power.
- Position for Natural Light: Place the TV in a way that takes advantage of natural light, reducing the need for higher brightness settings.
- Avoid Using the TV for Background Noise: Instead of leaving the TV on for background noise, consider using a radio or music streaming service that requires less power.
- Regularly Update Software: Keeping the TV’s software up to date can enhance energy efficiency and performance.
- Use a Power Strip: Connect your TV and other electronics to a power strip and turn it off when not in use to eliminate phantom loads.
Understanding the relationship between watts and electricity consumption is essential for managing your energy use and costs effectively. Knowing the wattage of your devices, such as your TV, can help you make more informed purchasing decisions and move your home in a more energy-efficient direction. At Santanna, we are committed to supporting homeowners like you in making informed decisions about energy consumption. We offer a range of energy solutions tailored to your needs and lifestyle.
There's peace of mind in knowing you'll pay the same monthly supply cost amount for your electricity or natural gas supply without any uncertainty — no matter what. Santanna's Unlimited Energy option *protects your bills from fluctuating supply charges no matter the changes in seasons. For over 35 years, Santanna has served customers in Illinois, Indiana, Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Ohio. Our mission is to provide innovative and cost-effective energy solutions that will help our customers achieve their energy goals.
* Restrictions apply. Enrollment based upon program eligibility. Customers using more than 125% of normal monthly usage as determined by Santanna may be required to switch plans.
Tyler is an experienced energy professional, having worked for Santanna Energy Services, for the past four years. He is passionate about renewable energy and believes that diversifying the energy grid is the key to a sustainable future. Tyler is dedicated to supplying consumers with the best possible energy solutions and works diligently to make sure that Santanna can deliver the highest quality service.